YDSE
Young’s double slit experiment:- (For interference light)
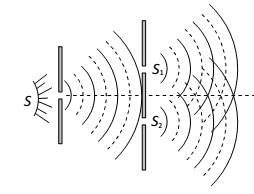
A mono chromatic source of light illuminates the slit S which sends out spherical wave fronts. These wave fronts reach S1 and S2 simultaneously which become the source of secondary wavelets.
When light waves from S1 and S2 arrive in phase (crest falls on crest & trough fall on through), constructive interference takes place and a bright band is formed on the screen.
When light waves arrive out of phase (crest falls on trough), destructive interference takes place and a dark band is formed on the screen.
Interference Fringes:- The alternate dark and bright bands on the screen are called as “interference fringes.”
Fringe width (β):- the distance between two successive dark or bright bands is called as “fringe width”.
Central maxima: the point ‘O’ on the screen at which the intensity of light is maximum, is called as central maxima.
Theory of Interference:-
Step-I:- To find the equation of resultant wave:
Let the displacements of the waves from two light sources are:
y1 = a1 sin wt
y2 = a2 sin (wt + φ)
Where
a1, a2 => Amplitudes of two waves
φ => constant phase difference by which 2nd wave leads the first.
According to superposition principle, the displacement of resultant wave is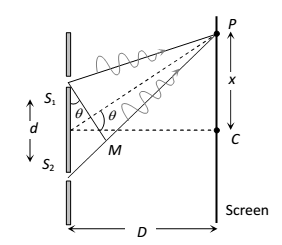
y = y1 + y2 = a1 sin wt + a2 sin (wt + φ)
y = a1 sin wt + a2 [ sin wt cos φ + cos wt sin φ]
y = (a1 + a2 cos φ) sin wt + a2 sin φ cos wt
y = A cons θ sin wt + A sin θ cos wt
let a1 + a2 cos φ = A cos θ ---------- (1)
& a2 sin φ = A sin θ -----------------(2)
y = A sin (wt + θ) [S.H.M equation]
Thus the resultant wave is a simple harmonic wave of amplitude A.
Step- II:-
Since A cos θ = a1 +a2 cos φ
A sin θ = a2 sin φ
Squaring and adding
A2 = a12 + a22 cos2 φ + 2a1 a2 cos φ + a22 sin2 φ
A2 = a12 + a22 (cos2 φ + sin2 φ) + 2a1 a2 cos φ
Step- III:-
To find the resultant Intensity:-
To find the resultant Intensity:-
Resultant intensity (I) at P ∝ (Amplitude)2 of resultant wave
∴ I ∝ A2 or I = KA2
Or I = K (a12 + a22 + 2a1 a2 cos φ)
I = K a12 + K a22 + 2K a1 a2 cos φ ------------ (1)
Intensity of individual waves, I1 = K a12 & I2 = K a22
∴ from (1)
Step IV:-
Conditions for constructive interference: (conditions of maxima)
Since
For constructive interference, I is maximum.
∴ cos φ = maximum = +1
∴ φ = 0, 2π, 4, ------------
i.e. φ = 2nπ n=0,1,2,3 -----------
path difference between the two waves reaching at point ‘P’ corresponding to phase difference φ is
Therefore interference will be constrictive (max. intensity) it the path difference between the waves is an integral multiple or λ.
Step V:
Condition for destructive interference: (condition of minima )
I is minimum ∴ cos φ = minimum = -1
= φ = π, 3 π, 5 π,-----------
Or φ = (2n + 1) π n=1,2,3,------------
Path difference between the waves corresponding to a phase difference φ is
∴ interference will be destructive min. intensity if the path difference between the waves is an odd integral multiple of λ/2.
Step VI:
Ratio of maximum and minimum intensity of light:
Since I = K (a12 + a22 + 2a1 a2 cos φ)
I = I max. when cos φ = +1
∴ I max. = K (a12 + a22 + 2a1 a2)
= K (a1 + a2)2
I = I min. when cos φ = -1
I min. = K (a12 + a22 - 2a1 a2)
= K (a1 - a2)2
Step VII:-
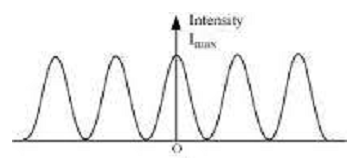
Intensity distribution curve of interference pattern:
The resultant intensity due to super position of two waves having constant phase difference φ is
If I1 = I2 = I0, then I = 2 I0 + 2 I0 cos φ = 2 I0(1 + cos φ)
For Maxima: φ = 2n π where n=0,1,2,3, --------
φ = 0, 2π, 4π, 6π,------------
∴ I = 2 I0(1+1) I =4I0 I0 = intensity of individual wave
For minima: φ = (2n+1) π where n = 0,1,2,3, --------
∴ φ = π, 3π, 5π ------------, I = 2I0 (1-1)
I = 0
i.e. all the Maxima ( Bright fringes ) are of constant intensity (4I0) and the Minima ( dark fringes ) are of ‘Zero’ intensity i.e. totally dark.
step VIII:-
Relation between intensity and width of source Intensity of light ∝ width of source:
let W1, W2 => width of two sources S1 and S2
∴ I1 ∝ W1 & I2 ∝ W2
∴ I ∝ (amplitude)2
∴ I1∝ a12
I2∝ a22
 SureDen
SureDen