Wavefront and Huygen's Principle
Wave Optics
Light:- light is a form of energy which gives the sensation of sight.
Optics:- optics is the branch of physics which deals with nature and properties of light.
Optics are two types:-
- Ray optics:- assumes that light consists of rays.
- Wave optics:- assumes that light is a form of energy which travels through a medium in the form of transverse waves.
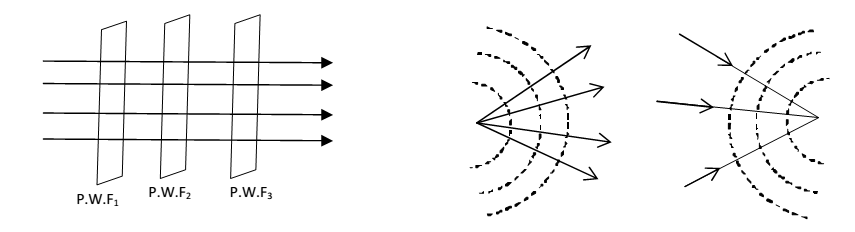
Wave front:- “A wave front is the continuous locus of all the particles of a medium vibrating in the same at a given instants.”
Explanation:- A source of light sends out disturbance in all the directions. This disturbance reaches in same time at all such particles which are at same distance from the source. These particles will vibrate in phase with each other. The locus of all such particles is called the wave front.
Types of wave front:- depending upon the shape of source of light wave front. Can be of three types.
-
Spherical wave front:- when the source of light is a point source, the wave front is a sphere with centre at the source.
- Cylindrical wave front:- when the source of light is linear (e.g. a slit), the wave front is cylindrical.
Plane wave front:- when the source of lights (points/linear) is at a very large distance, a small portion of spherical or cylindrical wave front appears to be plane and is known as plane wave front.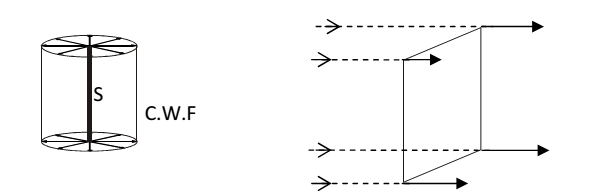
Rays of light:- “A ray of light is the path along which light is supposed to travel”. It is always drawn normal to the wave front.
Huygen’s principle:-
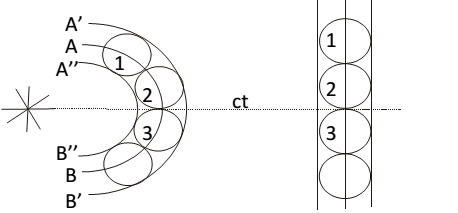
- Each point on a wave front (primary wave front) acts as a fresh source of light emitting secondary wavelets which are spherical and travel in all directions with velocity of light.
- A surface touching these secondary wavelets at any instant gives the wave front ( secondary wave front) at that instant.
In fig. (i)
AB = section of spherical wave front (primary) at any time
1,2,3 = points on primary wave front acting as fresh source of light.
A’B’ = forward secondary wave front.
A’’B’' =backward secondary wave front.
ct = distance travelled by secondary wavelet after time ‘t’.
In fig. (ii)
ABà plane wave front.
A’B’à forward secondary plane wave front.
A’’B’’ = backward secondary plane wave front.
 SureDen
SureDen