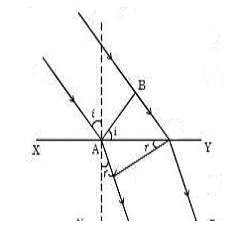
Law of Reflection and Refraction
Law’s of reflection (on the basis of Huygen’s principle)
let AB=> plane wave front incident on a plane mirror M1M2
According to Huygen’s principle, each point on the incident wave front act as a new source of light and emit secondary wavelet which travel with velocity of light (c).
Let t=> Time taken by the wavelets to reach from B to A’ and from A to B’.
A’B’=> Reflected plane wave front.
∴ BA’ = ct and AB’ = ct
∴ BA’ = AB’-----------(1)
In ∆ ABA’ :
In ∆ AB’A’ :
Putting the value of BA’ and AB’ in equation (1), we get
AA’ sin i = AA’ sin r
⟹ sin i = sin r
⟹ i = r
- i.e. angel of incidence = angle of reflection
- Further the incident waves, reflected waves and the normal all lie in the same plane (plane of paper).
Laws of refraction (On the basis of Huygen’s principle)
Let AB=> Plane wave front incident on surface XY separating the two media (air and glass).
Let µ=> Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air.
c=> Velocity of light in air.
ðœ—=> Velocity of light in glass.
Let t=> Time taken by the secondary wavelets reach from B to A’ and A to B’.
∴ BA’ = ct and AB’ = ðœ—t
In ∆ BAA’:
In ∆ BAA’:
Putting the value of BA’ and AB’ in equation (1) , we get
<= Snell’s haw of refraction.
- i.e. ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is constant(µ) for two media in contact.
- Further, the incident ray , refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same plane (plane of paper).
 SureDen
SureDen