Scattering
# Scattering:
“It is the phenomena in which light is emitted by the particles of the medium in all directions after absorption.”
# Rayleigh scattering law:
“According to this law, the intensity (I) of scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength (λ) of incident light.”
i.e. I ∝ 1/λ ∴ Red colour is least scattered (because of large wavelength)
Illustrations based on this law:
(i) Sky appears blue. Why?
Answer: As sun light travels through the earth’s atmosphere, it gets scattered by the large number of gaseous molecules of the atmosphere. According to Rayleigh scattering law, the intensity of blue colour (small wavelength) scattered is maximum. Thus the sky appears blue.
Note:
In the absence of earth’s atmosphere, the sky will appear black as no colour will be scattered in this condition.
(ii) Clouds are generally white. Why?
Answer: Clouds are at a lower height in the atmosphere. These contain large dust particles and water droplets etc. Their size is very large as compared to wavelength of incident light. So there is very little scattering of light. Hence the light which we receive through the clouds has all the colours of light. So we receive almost white light. Thus clouds are generally seen white in colour.
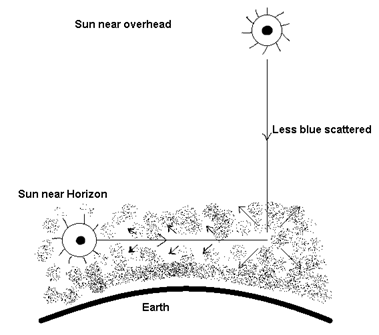
(iii) Sun looks reddish at the time of sun rise and sun set:
Answer: At the time of sun rise and sun set, the ray from the sun have to travel a larger part of atmosphere.
As λb < λr, ∴ according to Rayleigh scattering law, most of the blue light is scattered away & goes into space. Only red colour which is least scattered appears to come from the sun. Hence sun appears reddish.
(iv) Danger signals are Red. Why?
Answer: Since the wavelength of red light is maximum
∴ According to Rayleigh scattering law, red light is scattered through a small amount and hence it can be seen clearly from a large distance.
 SureDen
SureDen