Reflection of Light
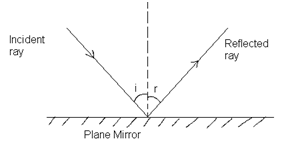
Reflection of light: Bouncing back of light rays after striking a surface in called as reflection.
Laws of Reflection:-
Angel of incidence = Angle of reflection i.e. ∠i = ∠r
- Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
Spherical mirrors:-
A spherical mirror is a part of hollow sphere whose one side is reflecting and other side is opaque.
Types:
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
Few definitions:
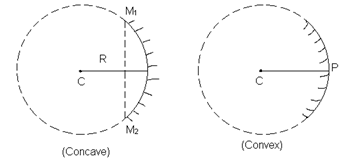
- Pole (P): centre of the mirror
- Centre of curvature (C): is the centre of sphere of which mirror is a part.
- Radius of curvature (R): radius of the sphere of which mirror is a part
- Principal Axis : is the line joining C and P.
-
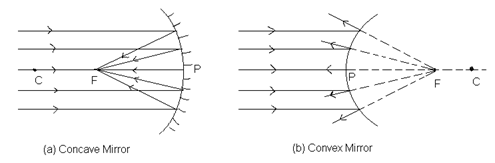
Principal Focus (F): is the point on the principal axis at which all rays parallel to principal axis converge or appears to converge after reflection from the mirror.
- Focal length (f): is the distance between principal focus and pole.
- Aperture: the diameter M1,M2 of spherical mirror is called aperture.
Relation between f and R :-
-
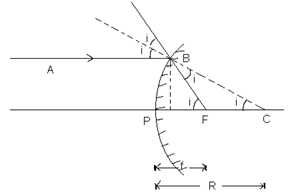
For concave mirror : consider a ray of light AB be incident on a concave mirror of small aperture.
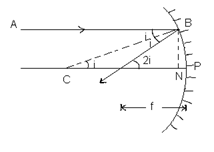
∠ABC = i = angel of incidence
∠CBF = ∠ABC = i (law of reflection)
In ΔCBN; tan i = (BN/NC) = (BN/PC) = (BN/-R) ------(i)
aperture is small
∴ NC ≈ PC ≈ -R
In Δ FBN; tan 2 i = (BN/NF)= (BN/PF)=(BN/-f) -------(ii)
Since aperture is too small ∴ i is too small
∴ tan i ≈ i, tan2i ≈ 2i
From (i) i = (BN/-R), from (ii) 2i = (BN/-f)
∴ (i/2i) = ((BN/R)/(BN/f)) = (f/R) ==> f = R/2
-
For convex mirror:
In ΔCBN, tan i = (BN/NC) = (BN/PC) = (BN/+R) --------(i)
In ΔFBN, tan 2i = (BN/NF) = (BN/PF) = (BN / +f) --------(ii)
i is too small, ∴ tan i ≈ i and tan 2i≈2i
From (i) i = (BN/R) From (ii) 2i = (BN/f)
(i/2i) = ((BN/R)/BN/f) ==> f = R/2
Uses of Spherical Mirrors:-
- Concave Mirrors:-
- Used in telescope.
- Used by dentists and E.N.T specialist to examine patients.
- Used as shaving mirrors, which gives an enlarged image of face.
- Used in cinema projectors.
- Convex Mirrors:-
- Used in automobiles because it produces the image smaller in size so that the field of view is more.
- Used as a reflector in street lamps. As a reflect, the light from the lamp diverges over a large area.
The sign conventions:
- All the distances are measured from the pole of a mirror.
- The distances measured in the direction of incident light are taken as +ve while those in opposite direction are taken –ve.
- Distance measured upward and normal to principal axis are taken as +ve and those measured m normally down ward are taken –ve.
 SureDen
SureDen