Rainbow
# Rainbow:
“A rainbow is a spectrum of sun light in the form of concentric coloured arcs in the sky formed immediately after rainfall.”
Essential conditions for observing a rainbow:
The observer must stand with his back towards the sun.
# Cause of formation of rainbow:
“A rainbow is formed due to the dispersion and total internal reflection of sun light by the water drops in the atmosphere. The water drops in the atmosphere behave like a prism.”
Sometimes two rainbows are seen:-
(i) Primary rainbow (ii) Secondary rainbow
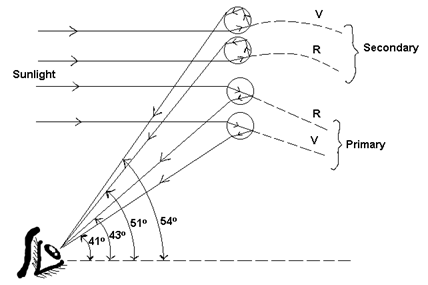
(i) Primary rainbow:
“Primary rainbow is formed due to two refractions and one T.I.R of the light incident on the droplets.”
Primary rainbow has violet colour on the outer edge and red colour on the inner edge. The violet rays come from the drops of water at an angle of 41° w.r.t. the horizon and the red rays at an angle of 43°. Other colours are formed between these two angles.
(ii) Secondary rainbow:
“Secondary rainbow is formed due to two refractions and two T.I.R. of the light incident on the droplets.”
Secondary rainbow has red colour on the inner edge and violet colour on the outer edge. The red rays come from the drops of water at an angle of 51° w.r.t. horizon and the violet rays come at angle of 54°.
Note:
It is found that the region between the two rainbows is comparatively darker and the region below the primary rainbow and above the secondary rainbow are comparatively brighter than the rest of the sky.
 SureDen
SureDen