Image formation by Mirrors
Rules for formation of image by spherical Mirrors:-
- A ray of light passing through centre of curvature ‘c’ gets reflected back along its own path.
- A ray incident parallel to the principal axis of the mirror, passes through its focus after reflection.
- A ray of light passing through the focus of a mirror becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection.
Types of images:
- Real Image: “A real image is formed when the rays of light after reflection from a mirror actually meet at a point in front of a mirror.”
It can be obtained on a screen. Areal image is always inverted w.r.t. object. Concave mirror gives a real image.
- Virtual Image: “A virtual image is formed when the rays of light after reflection from a mirror appear to meet at a point behind a mirror.”
It cannot be obtained on a screen. It can only be seen into the mirror. A virtual image is always erect w. r. t. object. A concave mirror forms a virtual image when the object is placed at distances less than the focal length.
Images formed by a concave Mirror:-
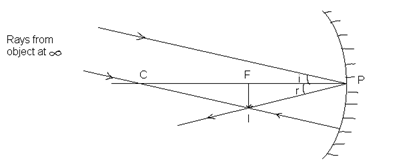
- When the object is at ∞:
Position image: At focus
Real, inverted, diminished.
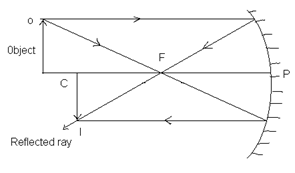
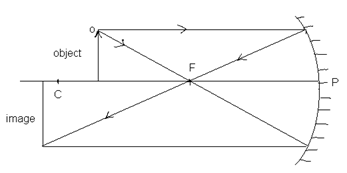
ii. When the object is beyond the centre of curvature:
Position of image: Between C & F
Real, inverted, diminished.
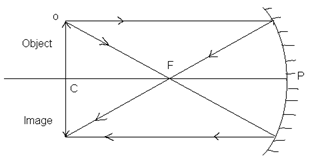
iii. When the object is placed at the centre of curvature:
Position of image: At C
Real, inverted, of the same size as that of object
iv. When the object is between C an F:
Position of image: Beyond C
Real, inverted, larger than the object.
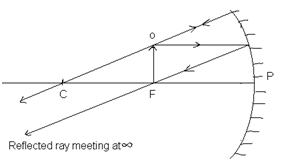
(v) When the object is at Focus(F):
Position of image: At ∞
Real, inverted and very large.
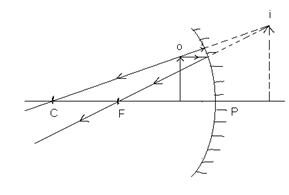
(vi) When the object is between the pole (P) and Focus (F):-
Position of image: Behind the mirror virtual, erect and larger than the object
# Image formed by a convex mirror:
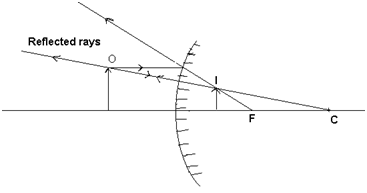
When the object is placed before a convex mirror:
Position of image: Virtual & erect behind the minor and smaller in size (always) As the object is taken away from the pole, the size of image goes on decreasing, At ∞, a point image is formed.
 SureDen
SureDen