Dispersion of Light
# Dispersion of light:
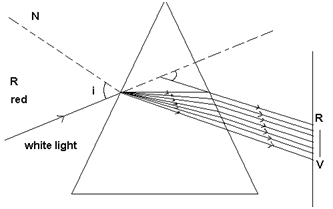
“It is the phenomena of splitting of a beam of white light into its constituent colours on passing through a prism.”
Spectrum:
“The band of seven colours obtained when a beam of white light is passed through a prism is called as spectrum of light.”
Band of colours:
V I B G Y O R
Violet Indigo Blue Green Yellow Orange Red
Cause of dispersion:
Each colour has its own wavelength.
Since δ = (µ - 1) A ∴ δ ∝ µ Also µ ∝ 1/λ2
∴ δ ∝ µ ∝ 1/λ2
Or δ ∝ 1/λ2
∴ Angle of deviation is inversely proportional to wavelength.
∴ Red colour (having maximum wavelength) undergoes minimum deviation and violent colour (having minimum wavelength) undergoes maximum deviation. Rest of the colours are deviated with angle between that for red and violet.
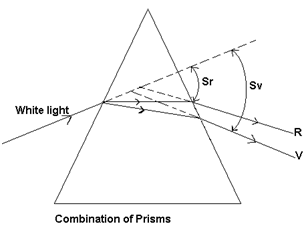
# Angular dispersion (θ)
“Angular dispersion for white light is the difference in the angles of deviation suffered by the two extreme colour (red and violet) after passing through the prism”
Angular dispersion θ = δv - δr
θ = (µv – 1)A – (µr – 1)A
θ = (µv - µr)A
δ = (µ - 1)A
δv = (µv - 1)A
δr = (µr - 1)A
∴ Angular dispersion depends on
(i) Angle of prism
(ii) Refractive index of material of prism
# Dispersive power of a prism (ω):
“Dispersive power of a prism is defined as the ratio of angular dispersion to the mean deviation produced by the prism”
∴ Dispersive power = Angular dispersion/Mean deviation (deviation for mean (yellow colour))
ω = (δv - δr/δy) = (µv - µr)A/µy – 1)A
ω = (µv - µr)/µy – 1
Note: (i) ω depends upon µ (ii) ω is independent of A.
 SureDen
SureDen