Electrostatics properties of a conductor
Electrostatics properties of a conductor:
When placed in electrostatic field, the conductors shows the following properties:
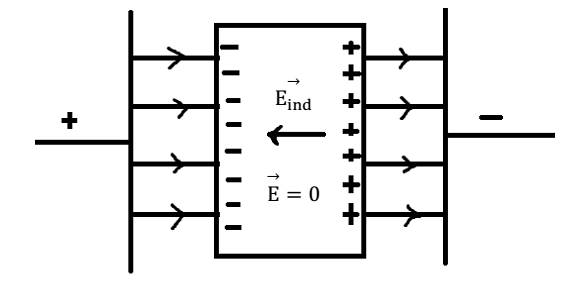
Net electrostatic field is zero in the interior of a conductor: When a conductor is placed in an external field, its free electrons begin to move in the opposite direction of external field. Negative charges are induced on the left end positive charges are induced on the right end of the conductor. The process continuous till the electric field Eind set up by the induced charges becomes equal and opposite to the field Eext. The net field inside the conductor at every point will be zero.
2.Just outside the surface of a charged conductor, electric field is normal to the surface: If the electric field is not normal to the surface, it will have a component tangential to the surface which will immediately cause the flow of charges, producing surface current, which is not possible at the equipontential surface.
3.The net charge in the interior of a conductor is zero and any excess charge resides at its surface: According to Gauss Theorem
as фE = 0, so q = 0 because electric field is zero interior to the conductor.
Hence there is no charge in the interior of the conductor.
4.Potential is constant within and on the surface of a conductor: Electric field at any point is equal to the negative gradient, i.e. E=dV/dr
But inside the conductor E=0 , so (dV/dr)=0 , hence V=constant.
5. Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to the surface charge density:
6. Electric field is zero in the cavity of a hollow charged conductor.
Electrostatic shielding:
The phenomenon of making a region free from any electric field is called electrostatic shielding.
Application of electrostatic shielding:
- In a thunderstorm accompanied by lightining, it is safest to sit inside a car, rather than near a tree or on the open ground. The metallic body of the car becomes an electrostatic shielding from lightining.
- Sensitive components of electronics devices are protected or shielded from electrical disturbances by placing metal shield around them.
- In a coaxial cable, the outer conductor connected to ground provides electrical shield to the signals by the central conductor.
 SureDen
SureDen