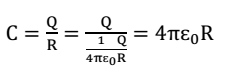Capacitance
Electrical capacitance of a conductor:
It is the measure of its ability to hold the electric charge.
If a charge Q on an conductor increases its potential by V, then
Q ∝ V
Or
Q = CV
The proportionality constant C is called the capacitance of the conductor.
Thus,
Capacitance = charge / potential difference
It depends upon the following factors:
- Size and shape of the conductor
- Nature of the surrounding medium
- Presence of the other conductors in its neighborhood.
Units of capacitance:
The SI unit of capacitance is Farad (F).
Dimension of capacitance:
Capacitance of an isolated spherical conductor:
Potential at any point on the surface of the spherical conductor of radius R will be
∴ capacitance of a spherical conductor is
Clearly, the capacitance of a spherical conductor is proportional to its radius.
Capacitor: A capacitor is an arrangement of two conductor separated by an insulating medium, that is used to store electric charge and electric energy.
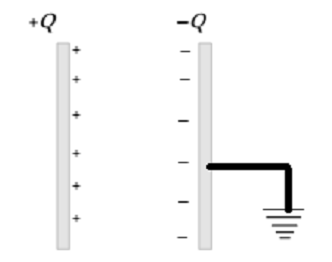
Principle of a capacitor: Consider a positively charged metal A and d place an uncharged plate B closed to it as shown in fig. due to induction the closer face of palate B acquires negatively charge and it farther face acquired the + charge. The negative charge on plate B tends to increase the potential on plate A while the positive charge on plate B tends to increase the potential on plate A. as the negative charge on plate B is closer to plate to A then +ve charge of plate B. So the net effect is that the potential of plate A decreases by small amount and hence its capacitance increases by small amount.
Now if the positive face of plate B is earthed. Its +charge gets neutralized due to the flow of electrons from the earth to the plate B the –ve charge on B is held in position due to positive charge on A. The –ve charge on B reduces the potential of A considerably and hence increases its capacitance by large amount.
 SureDen
SureDen