Electron Emission
Electron Emmision-The liberation of electrons from the surface of a metal due to any reason is known as Electron Emission.
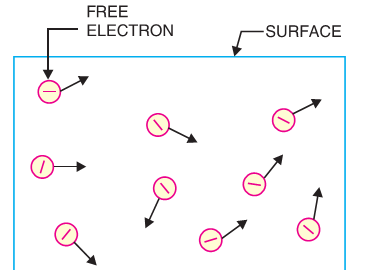
If we atke a piece of metal and investigate it at room temperature, the random motion of the electrons will be shown in Fig. However, these electrons are free to such extent that they may transfer from one atom to another within the metal but they cannot leave the metal surface to provide electron emission. It is because the free electrons that try to move out ,at the surface of metal find behind themselves a positive nuclei pulling them back . Thus at the surface of the metal , a free electron is attacracted by forces that prevent it to leave the metal. In other words, the metallic surface offers a barrier to these free electrons known as surface barrier.
However, if sufficient external energy is given by some means to the free electron, its kinetic energy is increased
and thus electron can cross over the surface barrier to leave the metal. This additional energy required by an electron to overcome the surface barrier of the metal is called work function of the metal
Work Function- It is the additional amount of energy required to remove an electron from the metal surface is known as Work Function.
The work function of pure metals varies (roughly) from 2eV to 6eV. Its value depends upon the nature of the metal, its purity and the conditions of the surface.
On the basis of energy(heat energy, energy stored in electric field, light energy or kinetic energy of the electric charges bombarding the metal surface) provided there can be different types of electron emission
Types of Electron Emission:
(i) Thermionic emission: If the metal is heated to a sufficient temperature (about 2500oC) so as to enable emission of the free electrons from the metal surface.
The number of electrons emitted depends upon the temperature. The higher the temperature, the greater is the emission of electrons.
(ii) Field emission: Here, a strong electric field is applied at the metal surface which pulls the free electrons out of the metal because of the attraction of positive field.
The strong the electric field, the greater is the electron emission.
(iii) Photoelectric emission:When electromagnetic radiations of suitable wavelength are incident on a metallic surface then electrons are emitted, this phenomenon is called photo electric effect.
The greater the intensity of light beam falling on the metal surface, the greater is the photoelectric emission. Photoelectric emission is utilized in photo tubes which from the basis of television and sound films.
(iv) Secondary emission: In this method, a high velocity beam of electrons is incident on the metal surface, these electrons strike the metal surface and provides the required energy to the free electrons to enalble to come out of metal surface.
. The intensity of secondary emission depends upon the emitter material, mass and energy of bombarding particles.
 SureDen
SureDen