Wheat Stone Bridge
Wheat stone Bridge: it is an arrangement of four resistances used to determine one of these resistances quickly and accurately in terms of remaining three resistances.
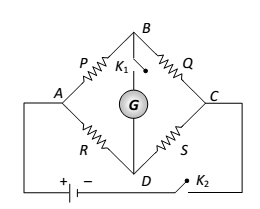
A wheat stone bridge consists of four resistance P,Q,R and S, connected to form the arms of a quadrilateral ABCD. A battery of emf ɛ is connected between points A and C and a sensitive galvanometer between B and D as shown in fig.
The resistance are so adjusted that no current flows through the galvanometer.
The bridge is then said to balanced condition P/Q = R/S
This is the wheat stone bridge principle.
Derivation: applying Kirchhoff’s law to the loop ABDA, we get
I1 P + Ig G – I2 R = 0
Where G is the resistance of the galvanometer
Similarly, applying KVL to loop BCDB, we get
(I1 - Ig)Q – (I2 + Ig)S – G Ig = 0
In the balanced condition of the bridge, Ig = 0, then above equations becomes
I1P – I2 R = 0
I1Q – I2 S = 0
Divide the above equations, we get
P/Q = R/S
This proves the condition for the balanced wheat stone bridge.
 SureDen
SureDen