Distance of Closest Approach
Distance of closest approach:
Estimation of two size of nucleus (by Rutherford experiments or distance of closest approach).
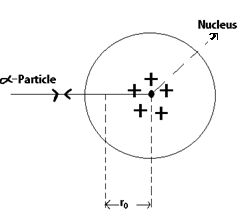
Suppose an ∝ - particle of mass m and initial velocity u moves directly towards the centre of the nucleus of an atom.
As it approaches the +ve nucleus, it experience a coulombic repulsions and its kinetic energy gets progressively converted in electrical energy.
At a certain distance ro from the nucleus the alpha particle stops for a moment and then begins to retrace its path. The distance ro is called the Distance of closest approach.
Initial kinetic energy of ∝ - particle
K∝ = ½ mu2
The electrostatic potential energy of alpha particle and nucleus at a distance ro is given by
V = K. (q1q2/ro) K. (2eZe/ro)
At a distance of ro, K∝ = U therefore
½ mu2 = K2Ze2/ro
ro = 4KZe2/mu2
Clearly radius of nucleus must be smaller than ro.
 SureDen
SureDen