Inner Transition Elements
Inner Transition Elements: (f-block elements) – Lanhanoides and Actinoides
The inner transition elements are divided into two categories Lanthanoide and actinoides. The Lanthanoides (At. no. 58 – 71) comes immediately after Lanthanum. They have general electronic configuration 4f1-145d0-16s2. The Actinoides (At. no. 90 – 103) comes immediately after actinium. They have general Electronic configuration 5f1-146d0-17s2. The electronic configuration of Lanthanoids and Actinoids is given below:
|
Lanthanoids Element Symbol At.No. Elect.Conf. [Xe] |
Actinoids Element Symbol At.No. Elect.Conf. [Rn] |
||||||
|
Lanthanum |
La |
57 |
5d16s2 |
Actinium |
Ac |
89 |
6d17s2 |
|
Cerium |
Ce |
58 |
4f25d06s2 |
Thorium |
Th |
90 |
6d27s2 |
|
Praseodynium |
Pr |
59 |
4f35d06s2 |
Protactinium |
Pa |
91 |
5f26d17s2 |
|
Neodymium |
Nd |
60 |
4f45d06s2 |
Uranium |
U |
92 |
5f36d17s2 |
|
Promethium |
Pm |
61 |
4f55d06s2 |
Naptunium |
Np |
93 |
5f46d07s2 |
|
Samarium |
Sm |
62 |
4f65d06s2 |
Plutonium |
Pu |
94 |
5f66d07s2 |
|
Europiom |
Eu |
63 |
4f75d06s2 |
Americium |
Am |
95 |
5f76d07s2 |
|
Gadolinium |
Gd |
64 |
4f75d16s2 |
Curium |
Cm |
96 |
5f76d17s2 |
|
Terbium |
Tb |
65 |
4f95d06s2 |
Berklium |
Bk |
97 |
5f96d07s2 |
|
Dysprosium |
Dy |
66 |
4f105d06s2 |
Californium |
Cf |
98 |
5f106d07s2 |
|
Holmium |
Ho |
67 |
4f115d06s2 |
Einsteinium |
Es |
99 |
5f116d07s2 |
|
Erbium |
Er |
68 |
4f125d06s2 |
Fermium |
Fm |
100 |
5f126d07s2 |
|
Thulium |
Tm |
69 |
4f135d06s2 |
Mendelevium |
Md |
101 |
5f136d07s2 |
|
Ytterbium |
Yb |
70 |
4f145d06s2 |
Nobelium |
No |
102 |
5f146d07s2 |
|
Lutetium |
Lu |
71 |
4f145d16s2 |
Lowrencium |
Lr |
103 |
5f146d17s2
|
- Oxidation State of Lanthanoides:- All lanthanoides exhibit a common stable oxidation state of +3. In addition of it some Lanthanoides show +2 and +4 oxidation states also. These oxidation states are shown by those elements which acquire f0, f7 or f14 configuration by doing so. Cerium (At. No. = 58) exhibits the +4 O.S. predominately.
- Atomic size (Lanthanoides Contraction):- In Lanthanoides series the nuclear charge increases in the atomic no. there is a progressive decrease in atomic as well as ionic radius (+3 O.S) form La to Lu. This regular decreases in size is called Lanthanoide contraction.
Cause of Lanthanoide Contraction:- As we move along the Lanthanoides series the nuclear charge increases by one unit each time. The new electrons is added into the same sub shell (4f) as a result of it, the attraction on the electrons by the nucleus increases and tends to decreases and tends to decrease the size. The increased nuclear charge due to imperfect shielding by the out wayed f-orbitals. Hence net result is the decrease in size of atoms (ions) from La to Lu.
Consequences of Lanthanoide Contraction:-
- There is a similarly in size of the elements belonging to 2nd and 3rd transition series elements even after the fact that size increases on moving down the group.
- The properties of Lanthanides are quite similar, but due to the small difference in their size the ability to form complexes vary which is used in separation of lanthanides.
- Basic Strength of hydroxides decreases from La(OH) to Lu(OH) to Lu(OH)3 because of the decreases in the size of trivalent ion from La to Lu.
- General Characteristics of Lanthanoids:-
Lanthnoids are silvery white soft metals and tarnish rapidly in air. They are hard with high M.Pt., good conductors of heat and electricity. Many trivalent cations are coloured both in solid state and in aq. Solution. La3+ show no colour because there are no unpaired electrons. The general reactions of lanthanoids is represented as: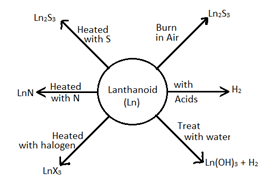
Use of Lanthanides:-
- Caeric Sulphate is used as oxidizing agent is volumetric analysis.
- An alloy of Lanthanide is used to make parts of jet engine.
- The oxides of Lanthanides are used in polishing mirror.
Cerium salts are used as dyes and catalyst.
 SureDen
SureDen