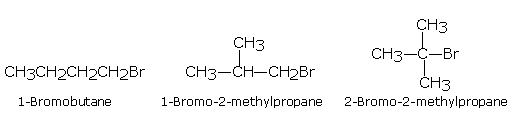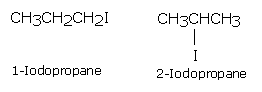Isomerism
Isomerism:
Isomerism is the phenomenon whereby certain compounds, with the same molecular formula, exist in different forms owing to their different organisations of atoms. The concept of isomerism illustrates the fundamental importance of molecular structure and shape in organic chemistry.
Isomerism in haloalkanes is of two types:
Chain isomerism
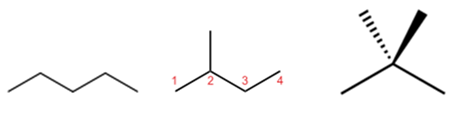
In chain isomerism, or skeletal isomerism, components of the (usually carbon) skeleton are distinctly re-ordered to create different structures. Pentane exists as three isomers: n-pentane (often called simply "pentane"), isopentane (2-methylbutane) and neopentane (dimethylpropane).
C4H9Br has three chain isomers,
Position isomerism
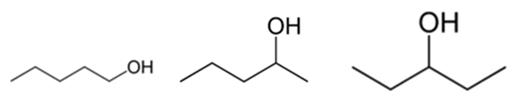
In position isomerism (regioisomerism) a functional group or other substituent changes position on a parent structure. In the table below, the hydroxyl group can occupy three different positions on an n-pentane chain forming three different compounds.
C3H7I has two position isomers:
 SureDen
SureDen