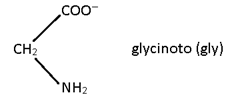Types of Legands
Type of Legands:-
Legands are e- donors means nucleophile and their denticity depends on presence of lone pairs which can be co-ordinated.
Generally legands are anion or natural but sometimes they can be positively charged.
According to denticity there are 6 type of legands from unidentate to hexadentate.
Unidentate
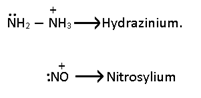
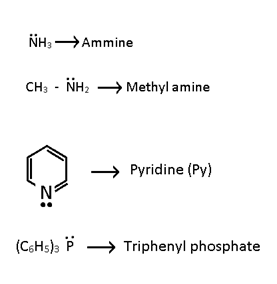
- Unidentate or Monodentate:- One lone pair donor.
b).Neutral:-
CO->Carbonyl
CS ->Thio Carbonyl
H2O->Aqua, Aquo
c) Negatively Charged:-
F-->Fluorido
Cl-->Clorido
Br-->Bromido
I- ->Iodido
OH- ->Hydroxo
NH2-->Amido
NO2-->Nitro
O‑ -NOO –-> Nitro
O--CN->Cyanoto
N- CO->Iso cyanoto
S-CN ->Thio cyanoto
N- CS ->Iso Thio cyanoto
N3-->Azido
PH2- ->Phosphido
C-N ->Isocyano
O2-2->Per oxo
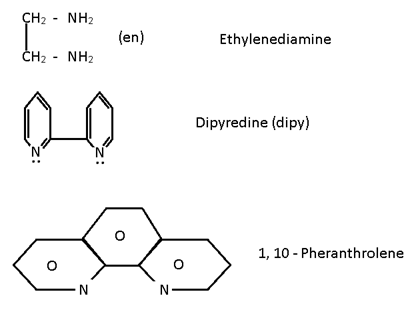
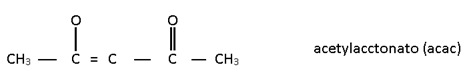
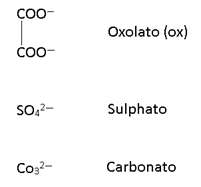
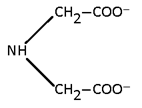
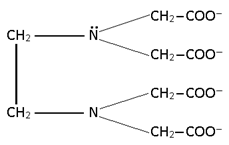
2. Bidentate:
Two lone pair donor
Note: All Bidentate have oxidation state -1.
And for (en) it is Zero.
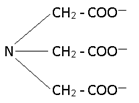
3 .Tridentate:-
Dien -> Diethylene triamine
Terpy --> Tripyridine
denticity means donation of lone pair.
nda --> nitrilodiacetato
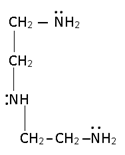
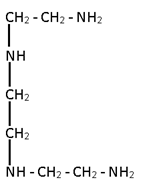
4. Tetra dentate
Tetra dentate or Quadridentate:-
Trien --> Triethylene tetramine
nitrilo triacetato
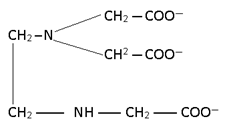
5. Penta dentate
ethylene diamine triacetate
6. Hexa dentate
Hexa dentate:- EDTA
Ethylene diamine tetra acetato
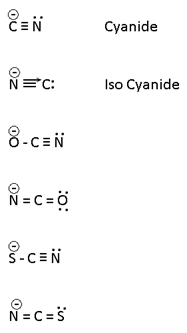
Ambidentate legand
In this more than one lone pair ore present at a time only one lone pair can be Co-ordinate their lone pair 3 or 4 membered ring is prepared which is highly unstable.
e.g.:-
All ambidentate are pseudo
Flexi dentate
Flexi dentate:- All polydentate legand are flexi legand because they can show more than one type of denticity.
Ethylene diamine is bidentate legand but can also behave as unidentate.
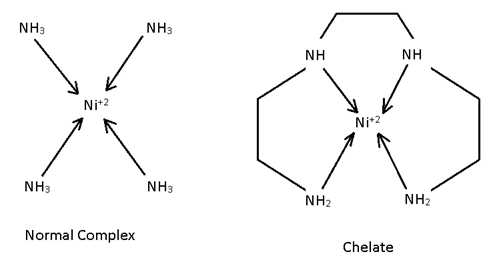
Chelating legand
Chelating Legand:-
It is non-cyclic legand but form cycle complex. Generally chilates are more stable than normal complexes but not always (because stabililty is decided by crystal filed theory).
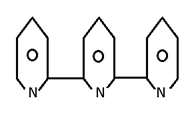
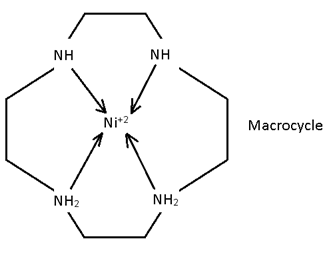
Macrocyclic legand
It is a cycle legand which form cyclic complex. Macrocyclic are more stable than chilates.
- Hb and chloropyll are Macrocycle.
- All crown ethers are macrocycle.
 SureDen
SureDen