Optical Isomerism
Optical Isomerism:-
Complexes having some molecular formula, same structure but different orientation about a central metal in 3-D space are optical isomers.
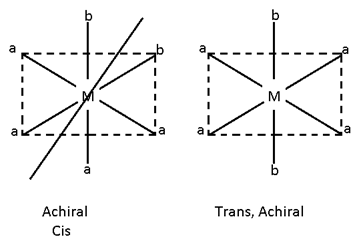
If any complex does not contain plane or centre of symmetry it is chiral complex. But if any one symmetry either plane or centre is present complex is definitely achiral.
Complex can be dextro or laevo but it is experimental observation. We can decide only optical activity not configuration by using symmetry.
Ma2b2c2 ==> Cis (active ), Trans (Inactive)
Ma2bcde ==> Cis (active), trans (Inactive)
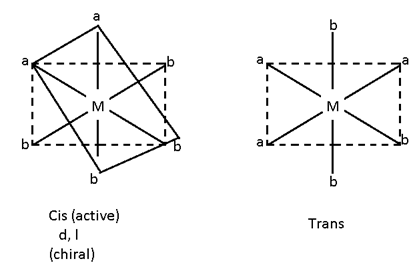
M (AA)2b2 ==> Cis (active), trans (inactive)
Mabcdef ==> Cis and trans both active.
M (AB)3 ==> Cis and trans both active.
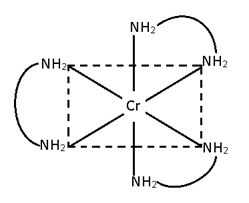
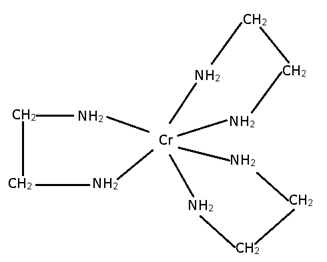
M (AA)3 ==> No geometrical, but optical
1.. Ma4b2
2.. Ma3b3
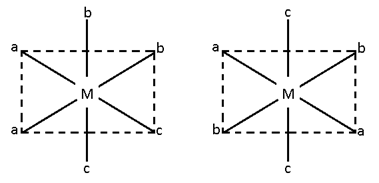
3. Ma2b2c2 - geometrical = 5
Optical = 2
Total stero = 6
Cis (active)
d, l
(Chiral)
- M(AA)3 [Cr (en)3]+3
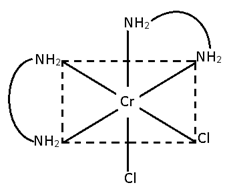
c)[Cr (en)2 Cl2]
2 geometrical
3 stereo
[M (AA)2 B2]
 SureDen
SureDen