Integrated Rate Equation
Integrated rate equation:- Rate = (-dA/dt) = k[A]
This is the differential rate equation. But this form is not convenient to the determination of rate law and order of reaction so we lntegrate the rate equations which provided the direct relation b/w time, concentration and rate constant.
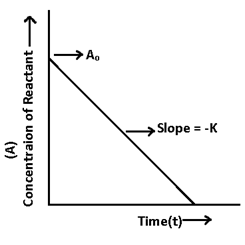
1. For zero order reaction:- Consider a reaction is of zero order.
A → Products
Rate = (-dA/dt) = k[A]o
-dA/dt = k
dA = -K dt
Integrate the above equation from 0 to t
∫dA = -K ∫dt
A = -Kt + I –(1) I = Integration constant
When t = 0, then A = A° at initial stages.
Put value of t and A in equation (1)
A° = -K x 0 + I = I
A° = I
Put value of I in equation (1)
A = -Kt + A° -(2)
Equation (2) is followed by all reactions of zero order
Y = mx =+ c
A = -Kt + A°
K = 1/t [Ao– A]
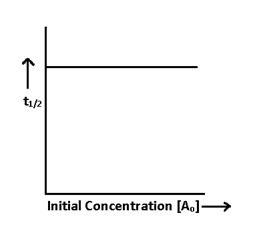
Half life Period:-
It is the time during which the concentration falls to half of the initial concentration.
when t = T1/2, then [A] = [A]o/2
so t = 1/k [Ao – A]
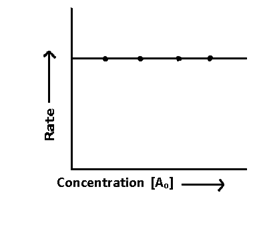
T1/2∝ Initial concentration or Ao
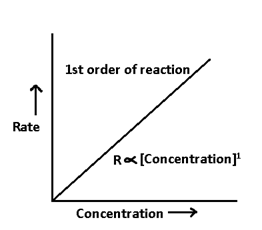
2. for First order reaction:- Consider a reaction of first order
A → product
-dA/dt = k [A]1
dA/A = -k dt
Integrate the above equation
∫(dA/A)= ∫ - k dt
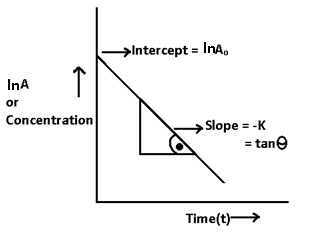
ln A = -Kt + I -(1)
When t = 0, then A = Ao at initial stages
Put value of t and A in equation (1)
ln Ao = -K x 0 + I
ln Ao = I
Put value of I in equation -(i)
ln A = -Kt + lnAo -(ii)
Equation (ii) must be followed by al reactions of first order
ln A = -Kt + ln Ao
y = -mx + c
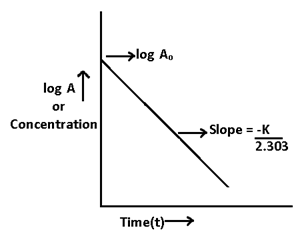
Equation (ii) can also be written as 2.303 log A = -kt + 2.303 log Ao -(iii)
Divide equation (iii) by 2.303
Log A = (-kt/2.303) + Log A0
t = (2.303/k)log(Ao/A)-------(iv)
Half life period:- when t = t1/2, then A = Ao/2
Put value of t and A In equation (iv)
t1/2 = 0.693/k
The half life period of first order reaction is independent of initial concentration.
Integrated rate equation for first order gas phase reaction
Consider a gas phase reaction of first order
A → B + C
Initially Po O O
At time t (Po - P) P P atm
Total pressure of reaction mixture (Pt) = Po - P + P + P = Po + P
P = Pt – Po
Rate of reaction = Po - P = Po - P+ + Po = 2 Po - Pt
 SureDen
SureDen