Collision theory of chemical reaction
Collision theory of chemical reaction:- According to it reactant molecules must collide with one another so as to change into products.
The number of collision taking place in one second in unit volnme of reactant mixture is 1025 to 1028, it is called Collision frequency.
If all these collisions were effective, then reaction should get complete with in a fraction of second but for a collision to be effective, it must have
1. Proper energy:- Energy should be equal or more than threshold energy.
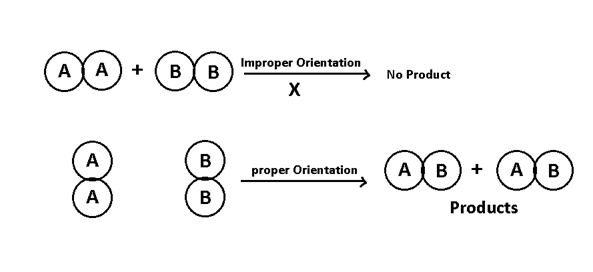
2. Proper orientation:- A2 + B2 → 2 AB
According to this theory rate of reaction is proportional to the fraction of effective collisions. More the effective collisions more will be the rate of reaction so more will be rate constant.
So k ∝ f f = fraction of effective collisions
k = z x z = collision frequency
k = total number of collisions x (number of effective collisions / total number of collisions)
K = number of effective collisions
 SureDen
SureDen