Structure of RNA and DNA
Structure of RNA and DNA:- The complete structure of Nucleic acid is discussed under the two heads:
Primary Structure
Secondary Structure.
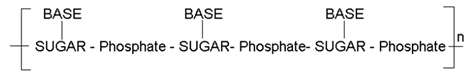
(1). Primary Structure:- Nucleic acids are polynucleotides. Due to polymerization the backbone of the nucleic acid consists of alternate sugar-phosphate residues. Each sugar on this back bone is further connected to one of the four nitrogeneous bases. Thus the sequence in which the four nitrogenous bases are attached to the sugar-phosphate backbone of a polynucleotide chain is called the primary structure of nucleic acid. Shown as:
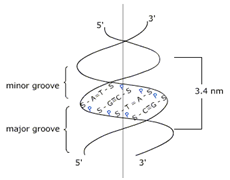
(2) Secondary Structure:- The secondary structure of DNA proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick, Consists two polynucleotide strands (chains). These strands run in opposite directions giving a right handed double α-helix structure to DNA. The two strands of the double helix are hold together at definite distances through hydrogen bonds.
These H-bonds are not random but are specific between a purine and a pyrimidine base pair. For example, ‘G’ always pairs with ‘C’ through three H-bonds and ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ through two H-bonds. The two strands of the double helix are complementary and not identical to each other.
Unlike DNA, RNA has only one strand.
 SureDen
SureDen