Structure of Proteins
Structure of Proteins:- The structure of proteins is quite complex. It can be studied under the following heads:-
1. Primary Structure:- The structure which shows the sequence of amino acids in protein is called the primary structure of proteins, this sequence (structure) is responsible for the specific biological function of the proteins e.g. The primary structure of hemoglobin is
-Val-His-Leu-Thr-Pro-Glu-Glu-Lys- (normal Hemoglobin)
However if just one amino acid in the sequence is changed, (Glutamic acid with valine) is produce in effective hemoglobin, found in patients of sickle cell anemia.
-Val-His-Leu-Thr-Pro-Val-Glu-Lys- (Sickle Cell Hemoglobin)
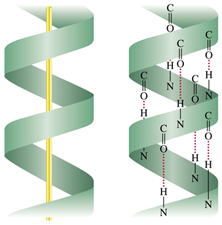
2. Secondary Structure:- The confirmation which the polypeptide chain assume as a result of hydrogen bonding is called secondary structure. Depending upon the size of R – group the following two different secondary structures are possible:-
(a) α- Helix Structure:- If the size of R- groups is quite large, the H- bonds (intermolecular) are formed between the C = O of one amino acid residue and the N-H of the fourth amino acid residue of the same protein molecule. This causes the polypeptide chain to coil up into a spiral structure, called right handed α-helix structure. Many fibrous proteins such as α-keratin in heir, nail, wood, skin; myosin in muscles have α-helix structure. The elasticity of these proteins is due to H-bonding.
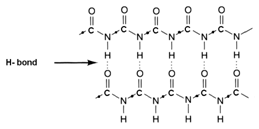
(b) β-Flat sheet of β-pleated sheet structure:-
If R groups are small, the polypeptide chain lie side by side in a zig – zag manner with alternate R-groups on the same side situated at fixed distances apart. The two such neighboring polypeptide chins are held together by intermolecular H-bonding resulting in the formation of a flat sheet structure as shown in figure.
The silk protein fibroin has β-pleated sheet structure, because of these structures silk fibers are not elastic.
3. Tertiary Structure of Proteins:- The tertiary structure of protein refers to its complete three dimensional structure. The tertiary structure refers to the manner in which the entire protein molecule folds up in the three dimensional space to give specific shape. This specific shape given to an amino acid sequence is called the native shape of the protein. The primary structure of protein dictates its tertiary structure.
 SureDen
SureDen