Proteins
PROTEINS
Proteins are the complex organic substances which are the basis of protoplasm and are found in all the living organisms. In general proteins are the polymers of α-amino acids.
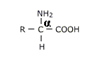
AMINO ACIDS:- Amino acids are the substituted carboxylic acids with the general formula.
Amino group (-NH2) at α- carbon forms the α-amino acids. These are the building blocks of proteins. There are about 20 naturally occurring α-amino acids which form almost all the animal and plant proteins. The α-amino acids differ in the nature of the side chain (R – group)
e.g. R is H in glycine, CH3 in Alanine, CH(CH3)2 in valine etc.
The amino acids which have two –COOH groups are called acidic amino acids e.g. Glutamic acid ((R = -CH2 – CH2 – COOH)) and aspartic acid (R = -CH2 – COOH). While the amino acids which have two –NH2 groups are called basic amino acids e.g. lysine (R = -CH2 – (CH2)3 – NH2)
Properties of α-amino acids:-
(1) Out of 20 naturally occurring amino acids, 10 amino acids can be synthesized by the body and remaining 10 are to be supplied by diet. The amino acids which are not synthesized by the body and must form an essential part of our diet called Essential Amino Acids. Apart from it six α-amino acids are present in special tissues.
(2) All amino acids expect Glycine contains at least one chirality center and hence are optically active. Almost all the naturally occurring α-amino acids are belonging to L-series whereas carbohydrates belong to D-series.
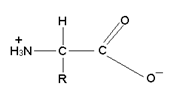
(3) Zwitter Ion:- The amino group of an amino acid is sufficiently basic and reacts with carboxylic acid group of same molecule to from an internal salt structure which is called Zwitter Ion. It is a dipolar ion with no net charge.
(4) Isoelectric Point:- The pH at which the structure of α-amino acid has no net charge is called Iso Electric point (pI). Each amino acid has a characteristic value of pI.
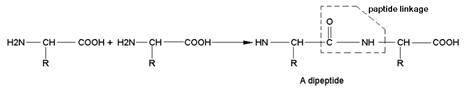
PEPTIDE LINKAGE OR PEPTIDE BOND:- Peptides are the amides formed by the condensation of an amino group of one α-amino acid with the carboxylic group of another molecule of the same or different α-amino acid. The linkages (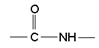 ) by which two amino acids are joined are called Peptide Linkage or Peptide Bond. e.g.
) by which two amino acids are joined are called Peptide Linkage or Peptide Bond. e.g.
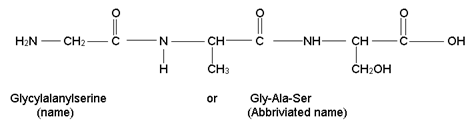
A simple convention is used to write the structure and name of a peptide. The amino acid unit having free –NH2 group is called N –Terminal and the amino acid unit having free –COOH group is called C – Terminal. In the structure N – end is written to the left and C – end is written to the right. The whole of the compound is written as derative of C – end and the suffix “-ine” is written while the suffix “-ine” of other acids is replaced by “-ly”. e.g. a tripeptide of glycine, alanine and serine is written as:
PROTEINS:- The name protein has been derived from Greek word “proteios” means “first” because it is prime substance to sustain life. In general proteins are polymers, (Truly macro molecules) of α-amino acids in which α-amino acids are joined by peptide linkage. Generally polymeric products of α-amino acids with molecular mass up to 10000 are called polypeptide and those having molecular mass greater than 10000 are called Proteins.
 SureDen
SureDen