Nucleic Acids
NUCLEIC ACIDS
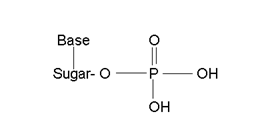
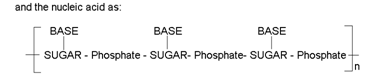
Nucleic acids are biopolymers. It constitutes an important class of bio molecules, which are found in the nuclei of all living cells in the form of nucleoproteins. They are also called polynucleotides, since the monomer unit of nucleic acid is a nucleotide. Each nucleotide is made up of three parts i.e. a sugar molecule, a heterocyclic nitrogeneous base and phosphoric acid. Thus in general, a nucleotide may be represented as:
Composition of nucleic acid:- All the nucleic acids on complete hydrolysis give a mixture of three different type of compounds (1) Phosphoric acid (2) A sugar and (3) A number of Nitrogeneous bases
(1) Phosphoric Acid:- All the nucleic acid contains phosphoric acid H3PO4
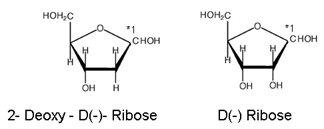
(2) Sugar:- Two pentose (sugars) have been isolated from hydrolysis of nucleic acids, these are:
These represent furanose structure of two sugars. * at C1, shows that both the sugars can exist as α- and β forms.
(3) A number of Nitrogeneous bases:- There are two different classes of nitrogen bases which been isolated form hydrolysis of nucleic acids. These are:
(a) Pyrimidines (b) Purines
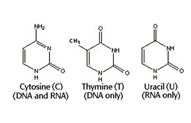
(a) Pyrimidines:- Primidines are the bases whose basic structure resembles withPyrimidine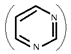 . There are 3 Pyrimidine bases; these are Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U).
. There are 3 Pyrimidine bases; these are Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U).
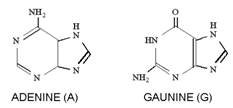
(b) Purines:- Purines are the bases whose basic structural unit resembles Purine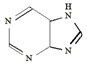
There are 2 Purine bases; these are Adenine (A) and Gaunine (G).
 SureDen
SureDen