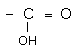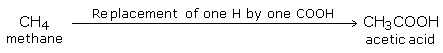Carboxylic Acids
Introduction, nomenclature, examples of aliphatic carboxylic acids
Organic compounds that contain one or more carboxyl groups, (-COOH) have acidic properties and are known as carboxylic acids. The word carboxyl rightly represents this functional group in the sense that it is a combination of the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group as shown below:
They may be considered as carboxyl derivatives of hydrocarbons where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by carboxyl groups.
For example:
Acids containing one carboxyl group are called monocarboxylic acid and those with two or three carboxyl groups are called di- and tri- carboxylic acids respectively.
Introduction of carboxylic acids
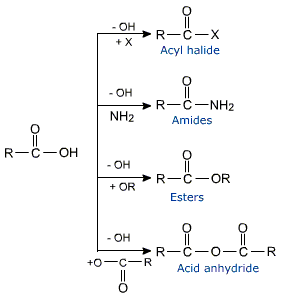
Replacement of hydroxyl group in carboxylic acids with a halogen, carboxylate, alkoxy or amino group gives functional derivatives of carboxylic acid known as acyl halides, acid anhydrides, esters or amides respectively.
 SureDen
SureDen