Preparaton of Ethers
Preparation of ethers
- By Dehydration of Alcohols:
Two molecules of alcohol when heated with conc. H2SO4 or conc. H3PO4 may loose one molecule of water to give an ether .
This method involves heating of excess of primary alcohol to get symmetrical ether.
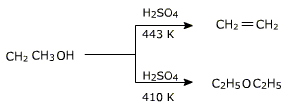
The formation of reaction product, alkene or ether depends on the reaction conditions.
In this reaction alcohol has to be used in excess and the temperature has to be maintained around 413 K. If alcohol is not used in excess or the temperature is higher, the alcohol will preferably undergo dehydration to yield alkene.
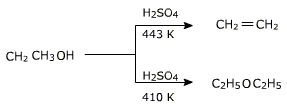
If ethanol is dehydrated to ethene in presence of sulphuric acid at
433 K but as 410 K ethoxyethane is the main product.
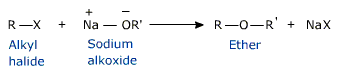
- Williamson Synthesis of Ethers:
Heating of alkyl halide with sodium or potassium alkoxide gives ether .
It is an important laboratory method for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
Ethers containing substituted alkyl groups (secondary or tertiary) may also be prepared by this method.
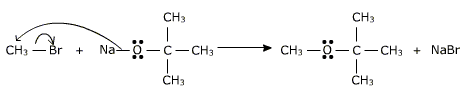
The reaction involves a nucleophilic substitution of halide ion by an alkoxide ion
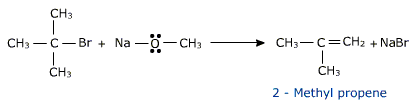
The reactivity of primary alkyl halide is in the order CH3>CH3-CH2> CH3-CH2-CH2 and the tendency of the alkyl halide to undergo elimination is 3>2>1.hence for better yield the alkyl halide should be primary and the alkoxide be secondary or tertiary .
3) ALKOXY MERCURATION DEMERCURATION :
It is another method for synthesizing ethers . The reaction of alkene with an alcohol in the presence of mercury salts such as mercuric salts such as mercuric acetate or trifluoro acetate leads to an alkoxy mercuric intermediate which upon reaction with sodium borohydride yields an ether .
Laboratory preparation of ethoxy ethane form ethanol
Laboratory preparation of ethoxy ethane is done by heating excess of primary alcohol with conc.
H2SO4 at 413 K to get symmetrical ether.
The formation of reaction product, alkene or ether depends on the reaction conditions.
In this reaction alcohol has to be used in excess and the temperature has to be maintained around 413 K. If alcohol is not used in excess or the temperature is higher, the alcohol will preferably undergo dehydration to yield alkene
If ethanol is dehydrated to ethene in presence of sulphuric acid at
433 K but as 410 K ethoxyethane is the main product.
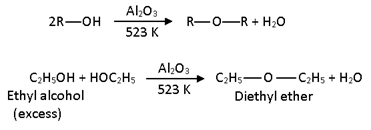
4 ) CATALYTIC Dehydration :
Inter molecular dehydration of primary alcohol is also affected by passing the vapours of an alcohol is also affected by passing the vapours of an alcohol over aluminia or thoria at 523k under pressure .
 SureDen
SureDen