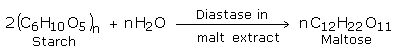Preparation of Ethanol
Industrial preparation of ethanol
Ethanol can be manufactured by the fermentation of:
- Molasses
- Starch
Slow decomposition of organic compounds is called fermentation. This is the principle behind souring of milk, batter, putrefaction of meat, and preparation of wine and vinegar. Fermentation was the earliest method used for preparing alcohol in industries. This is still used for the manufacture of alcohol and alcoholic drinks like beer, wine, brandy, etc,.
Raw materials
Cheap starchy materials like potatoes, maize, barley, rice etc.
OR Molasses, a byproduct of sugar industry.
From Molasses
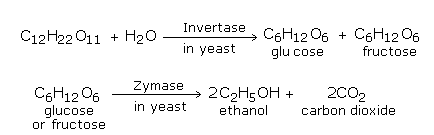
The syrup left after the separation of cane sugar or beet sugar crystals from the concentrated sugar cane juice is called molasses. It is a dark coloured syrupy mass and contains about 30% of uncrystallizable sucrose and about 32% of invert sugar (a mixture of glucose and fructose). The different steps in the manufacture of ethanol by fermentation of molasses are:
Highly Magnified Yeast Cells
The dilute solution obtained as above is taken in big fermentation tanks and some yeast is added (5% by volume). The temperature is maintained at 330K and the mixture is allowed to stand for a few days. Fermentation sets in and the enzyme (organic catalyst) invertase present in yeast, converts sucrose into glucose and fructose. Zymase, another enzyme present in yeast converts glucose and fructose into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
The fermentation is complete in 3 days. The carbon dioxide obtained as byproduct is recovered and can be sold.
Distillation
The fermented liquor contains 9-10% of ethanol and is called wash or wort.It is distilled in a Coffey still (Distillation of wash in a Coffey still) to remove water and other impurities present in wash. The Coffey still consists of two tall fractionating columns with perforated plates. These columns are called the analyser and the rectifier.
From Starch
Starchy raw materials
Wheat, barley, rice, maize and potatoes.
Conversion of starch into maltose
Conversion of starch into maltose or saccharification is carried out as follows:
Malting
Moist barley is allowed to germinate in dark at 290K. Germinated barley is called Malt and this is heated to 330K (to stop further germination). It is then crushed and extracted with water. This Malt extractcontains the enzyme diastase.
Hydrolysis
Mash and malt extract are treated together at 320-330K. In about half an hour, hydrolysis is complete and maltose is formed.
 SureDen
SureDen