Isomerism
Isomerism of alcohols
Alcohols exhibit following types of isomerism:
1. Chain isomerism
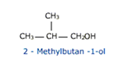
Alcohols containing four or more carbon atoms exhibit this type of isomerism in which the isomers differ in the chain of carbon atoms attached to the hydroxyl group.
CH3 — CH2 — CH2 — CH2OH
Butan – 1 – ol
2. Position isomerism
Alcohols with three or more carbon atoms can exhibit position isomerism. In this type of isomerism the isomers differ in the position of hydroxyl group when carbon chain is same.
CH3 — CH2 — CH2OH
Propan -1- ol
3. Functional isomerism
Saturated monohydric alcohols having two or more carbon atoms show sunctional isomerism with ethers .
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2OH
Butan -1- ol
CH3 — CH2 — O — CH2CH3
Ethoxyethane
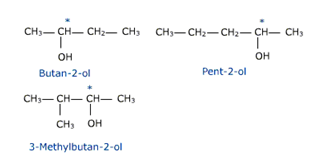
4. Optical isomerism
Alcohols containing chiral centre exhibit enantiomerism or optical isomerism. The optical isomers can rotate the plane of plane polarized angles in different directions.
* represents an asymmetric carbon atom.
 SureDen
SureDen