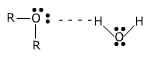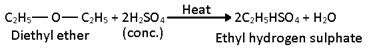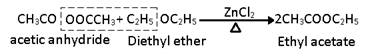General Characteristics of Ethers
GENERAL CHARACTERSTICS OF ETHERS :
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES :
Physical properties of ether :
a) Physical state
1)Ethers are colourless, pleasant smelling, volatile liquids with typical ether smell.
2) Ethers are sparingly soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding .
b) Boiling points
Ethers have much lower boiling points as compared to alcohols because they show no hydrogen bonding within them selves as alcohols .
c) Solubility
Ethers containing upto 3 carbon atoms are soluble in water, due to their hydrogen bond formation with water molecules.
The solubility decreases with increase in the number of carbon atoms. The increase in the hydrocarbon of the molecule decreases the tendency of H-bond formation.
Ethers are soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, benzene, etc.
d) Ethers having bond angle C-O-C to about 110 degree and thus , dipole moment of two C-O bond does not cancel out each other .
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES :1
Chemical properties:-
- Ethers are chemically less reactive as they do not have any active functional group.
- They do not react with bases, reducing agents, oxidizing agents and active metals, etc. under ordinary conditions.
- Ethers undergo chemical reactions under specific conditions.
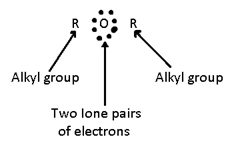
The electronics formula of an ether can e represented as:
The properties of ethers are due to alkyl groups, Ione pairs of electrons on oxygen atom and cleavage of C – O bond.
- Alkyl groups show substitution reaction like alkanes.
- Due to the presence of two Ione pairs of electrons, ethers form oxonium salts with mineral acids.
- The C – O bond is not so stable as C – C bond. The C – O bond is ruptured in the presence of a number of reagents.
- Ring substitution in aromatic ethers.
1. Reactions Due to Alkyl Groups:-
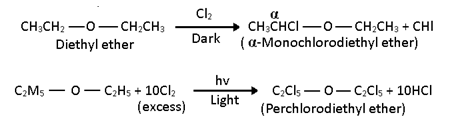
i) Halogenation:-
1. Ethers undergo substitution at alkyl radicals when reacted with chlorine or bromine, in the absence of sunlight to form halogenated substituted ethers.
2. Usually the hydrogen at the α-carbon is displaced most readily.
ii) Burning:-
1. Ethers are highly imflammable.
2. They burn, like alkanes to produce carbon dioxide and water.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES 2
2. Reactions Due to Ethereal Oxygen:-
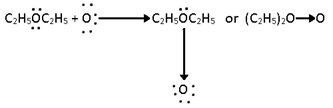
i) Peroxide formation:-
1. Ethers add up atmospheric oxygen or ozonised oxygen through co-ordination of one of the lone pair of ethereal oxygen to form peroxides in presence of sunlight or ultraviolet light.
2) The peroxide of diethyl ether is heavy, pungent oily liquid unstable compound and decomposes violently on heating
ii) Salt formation:-
1. Due to the presence of Ione pair of electrons on oxygen atom, behaves as Bronsted- Lowery base or Lewis Base.
2. It stable oxonium salts with cold concentrated mineral acids at low temperature.
3. Reactions Involving Cleavage of Carbon-Oxygen bond:-
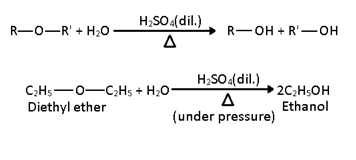
i) Hydrolysis (Action of dilute H2SO4): When heated at high temperature with dilute sulphuric acid under pressure ethers are hydrolysed to the corresponding alcohols.
ii) Action of conc. H2SO4: When warmed with concentrated sulphuric acid, ethers from alcohol and alkyl hydrogen sulphate.
iii) Action of hydroidodic acid:-
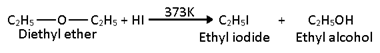
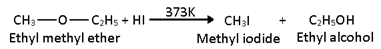
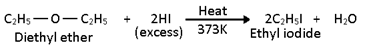
1. Ethers are readily attacked by high concentration of HI or HBr at 373 K to give a mixture of alkyl iodide and alcohol.
For symmetrical ether:-
For mixed ether:-
When heated with excess of HI, the alcohol first formed reacts further with HI to form corresponding alkyl iodide.
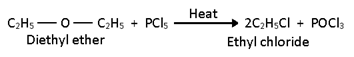
iv) Action of PCl5:-
On heating with PCl5, it also brings in the cleavage of carbon-oxygen bond of ethers to form alkyl chlorides.
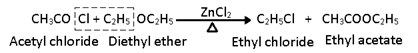
v) Reaction with Acetyl chloride and acetic anhydride:
With acid anhydride esters are formed in presence of ZnCl2.
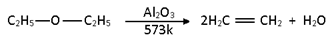
vi) Dehydration: When ether vapours are passed over heated alumina, dehydration of ether occurs to form alkenes.
 SureDen
SureDen