Types of Pollination
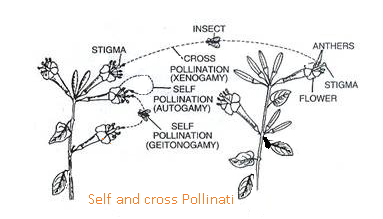
1. AUTOGAMY: Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of the same flower.
REQUIREMENT:-
- Synchrony in pollen release and stigma receptivity.
- Closeness of stigma and anther
Some plants such as Viola , Oxalis, and Commelina produce two types of flowers
- Chasmogamous flowers- flowers with exposed anthers and stigma.
- Cleistogamous flowers-flowers which do not open at all
Cleistogamy is disadvantageous because there is no chance of variation.
Autogamy takes place by three methods.
a)Homogamy:
The anthers and stigmas of chasmogamous or open flowers are brought together by growth, bending or folding.
b) Cleistogamy: The flowers are intersexual. They remain closed causing self pollination.
c) Bud Pollination: Anthers and stigmas of intersexual or perfect flowers ripen before the opening of the buds so that self pollination takes place as a rule, e.g., Pea, Wheat, and Rice
2. GEITONOGAMY : Pollination in which the transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of another flower of the same plant. This is genetically similar to autogamy because pollination is taking place in the same flower.
Example:- Cucurbits
3. XENOGAMY: It is the Pollination in which transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of another flower of different plant
Here genetically different pollen grains are brought to the stigma.
 SureDen
SureDen