Living organism cope with environment
How do Living Organisms Cope with Environment?
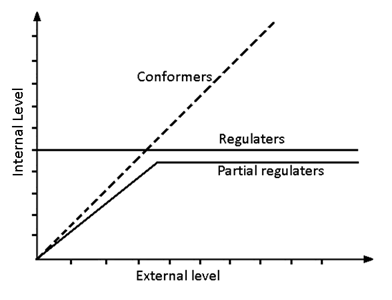
(i) Regulaters:-
- Some organisms maintain homeostasis by physiological and behavioural means.
- All birds and mammals and few lower vertebrate and invertebrate species maintain homeostasis by thermoregulation and osmoregulation.
- The success of mammals is largely due to their ability to maintain a constant body temperature.
- In summers, when outside temperature is more than our body temperature, we sweat profusely and the resulting evaporative cooling brings down the body temperature.
- Whereas in winters, when temperature is lower we shiver, a kind of exercise that produces heat and raises the body temperature.
(ii) Conform
- Majority (99%) of animals and nearly all plants cannot maintain a constant internal environment.
(iii) Migration
- The temporary movement of organisms from the stressful habitat to a more hospitable area and return when favourable conditions reappear, is called migration.
- E.g.:- In winter, famous Keolado National Park (Bharatpur) in Rajasthan hosts thousands of migratory birds coming from Siberia and other extremely cold northern regions.
(iv) Suspend
- Some bacteria, fungi and lower plants, under unfavourable conditions slow down metabolic rate and form a thick – walled spore to overcome stressful conditions.
- These spores germinate under coming of suitable environment.
- The animals that fail to migrate might avoid the stress by escaping in time, e.g., bear goes into hibernation during winter.
- Snail and fish go into aestivation to avoid summer.
- Zooplanktons under unfavourable conditions enter diapauses, a stage of suspended development.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen