Infectious diseases
Infectious diseases:
These are further divided into five classes:
1) Bacterial infectious diseases: For example; typhoid, pneumonia, diphtheria, plague, bacterial dysentery, laprosy, syphilis.
(i) Typhoid
It is caused by pathogenic bacterium Salmonella typhi and spread by contaminated food and water. It generally enters the small intestine and then migrates to other organs through blood. Typhoid fever can be detected by Widal test. Mary Mallon, called Typhoid Mary, was a cook and a typhoid carrier who continued to spread the disease for several years through the food prepared by her.
Symptoms
(a) Constant high fever
(b) Weakness
(c) Stomach pain and Constipations
(d) Headache
(e) Intestinal swellings
(ii) Pneumonia
It is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza. They infect alveoli (air-filled sacs) of the lungs where the alveoli get filled with a fluid resulting in the decreases of respiratory efficiency of the lungs. It is spread by inhaling droplets from infected persons and sharing their effected glasses and utensils.
Symptoms
(a) Fever
(b)Cough and chills
(c) Headache
(d) Lips and finger nails may even turn gray to bluish in colour.
2) Viral infectious diseases: For example; common cold, polio, chickengunia, influenza, chicken pox, small pox, herps, mumps, dengue, hepatitis-A and B, AIDs.
Common cold
It is caused by a group of viruses called rhino viruses. These viruses infect the nasal epithelium and respiratory passage but not the lungs. Their attack lasts for about 3-7 days. It spreads by contaminated objects like pens, books, cups, etc., and from cough and sneeze droplets from an infected person.
Symptoms
(a) Nasal congestion and discharge
(b) Dry throat and Hoarseness
(c) Cough
(d) Headache and Tiredness
3) Protozoan infectious diseases: For example; amoeboisis(enteritis), malaria.
(i) Malaria:
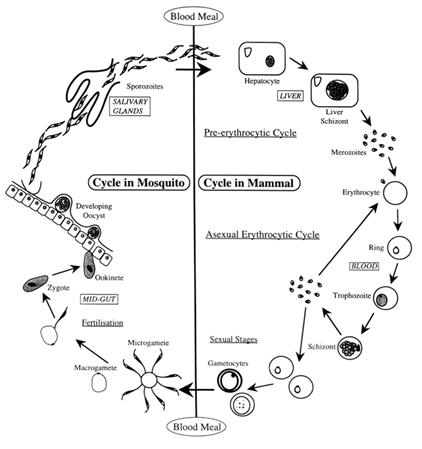
It is caused by a protozoan Plasmodium (P. vivax, P. malaria and P. falciparum). P. falciparum caused the most serious and fatal malignant malaria. The vector of Plasmodium is female Anopheles mosquito which transfers the sporozoites (infections form).
The life cycle of Plasmodium:
- Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites (infectious form) through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
- The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture.
- The rupture of RBCs is associated with release of a toxic substance, haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days.
- When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person, these parasites enter the mosquito’s body and undergo further development.
- The parasites multiply within them to form sporozoites that are stored in their salivary glands.
- When these mosquitoes bite a human, the sporozoites are introduced into his/ her body, thereby initiating the events mentioned above.
- The malarial parasite requires two hosts – human and mosquitoes – to complete its life cycle, the female Anopheles mosquito is the it.
(ii) Amoebic dysentery (Amoebiasis)
It is caused by an intestinal endoparasite, Entamoeba histolytica, found in large intestine of humans. Housefly acts as mechanical carrier and transmits the parasite from faeces of infected person to the food. Infection takes place through contaminated food and water.
Symptoms
(a) Abdominal pain(b) Constipation
(c) Cramps(d) Stools with excess mucous and blood clots.
4) Fungal infectious diseases: For example; ringworm and athlete’s foot.
Ringworm
It is caused by fungi of genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton. Human infection occurs either through contact with an infected person or from soil. It also spreads through towels, clothes, combs, etc., of the infected persons.
Symptoms
Dry and scaly lesions on skin, nails and scalp with intense itching.
5) Helminthic infectious diseases: For example; ascariasis, filariasis(eliphantiasis), taeniasis.
(i) Ascariasis
It is caused by an intestinal endoparasite of human, Ascaris lumbricoides, commonly called roundworm.Eggs of parasite are excreted along with faces of infected person, which contaminate, water, soil and plants. Infection takes place through contaminated vegetables, fruits and water.
Symptoms
(a) Abdominal pain
(b) Indigestion
(c) Internal bleeding that causes anaemia(blood loss)
(d) Muscular pain
(e) Fever
(f) Nausea and headache
(g) Blockage of the intestinal passage.
(ii) Filariasis(Elephantiasis)
It is caused by filarial worms, Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi. Female Culex mosquito is the vector.
Symptoms
(a) Inflammation of organs in which they live
(b) Blockage of lymph vessels of lower limbs resulting in swelling. Lower limbs appear like legs of elephant, thus the name.
(c) Genital organs may also be affected, leading to deformation.
 SureDen
SureDen