SEPARATION AND ISOLATION
Separation and Isolation of DNA Fragments (Gel Electrophoresis)
- Gel electrophoresis is a technique for separating DNA fragments based on their size.
- Firstly, the sample DNA is cut into fragments by restriction endonucleases.
- The DNA fragments being negatively charged can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix.
- Commonly used matrix is agarose, which is a natural linear polymer of D – galactose and 3, 6 – anhydro – L – galactose which is extracted from sea weeds.
-
The DNA fragments separate – out (resolve) according to their size because of the sieving property of agarose gel. Hence, smaller the fragment size, the farther it will move.
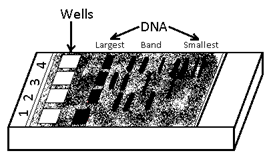
- Theseparated DNA fragments are visualised after staining the DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation.
- The DNA fragments are seen as orange coloured bands.
- The separated bands of DNA are cut out and extracted from the gel piece. This step is called elution.
- The purified DNA fragments are used to form recombinant DNA which can be joined with cloning vectors.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen