Standing Waves in Open Organ Pipes
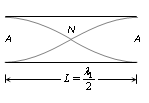
General formula for wavelength
This is called fundamental frequency and the note so produced is called fundamental note or first harmonic.
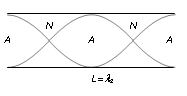
(2) Second normal mode of vibration
This is called second harmonic or first overtone.
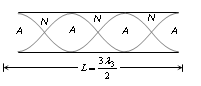
(3) Third normal mode of vibration
This is called third harmonic or second overtone.
Important Points
(i) Comparison of closed and open organ pipes shows that fundamental note in open organ pipe has double the frequency of the fundamental note in closed organ pipe
Further in an open organ pipe all harmonics are present whereas in a closed organ pipe, only alternate harmonics of frequencies
etc are present. The harmonics of frequencies 2n1, 4n1, 6n1 …… are missing.
Hence musical sound produced by an open organ pipe is sweeter than that produced by a closed organ pipe.
(ii) Harmonics are the notes/sounds of frequency equal to or an integral multiple of fundamental frequency (n). Thus the first, second, third, harmonics have frequencies
(iii) Overtones are the notes/sounds of frequency twice/thrice/ four times the fundamental frequency (n)
and so on.
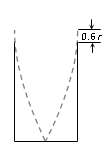
(iv) In organ pipe an antinode is not formed exactly at the open end rather it is formed a little distance away from the open end outside it. The distance of antinode from the open end of the pipe is known as end correction.
 SureDen
SureDen