Principle of Superposition
The displacement at any time due to any number of waves meeting simultaneously at a point in a medium is the vector sum of the individual displacements due each one of the waves at that point at the same time.
If………. are the displacements at a particular time at a particular position, due to individual waves, then the resultant displacement.
Examples
(i) Radio waves from different stations having different frequencies cross the antenna. But our T.V/Radio set can pick up any desired frequency.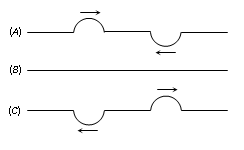
(ii) When two pulses of equal amplitude on a string approach each other [fig. (A)], then on meeting, they superimpose to produce a resultant pulse of zero amplitude [fig (B)]. After crossing, the two pulses travel independently as shown in [fig (C)] as if nothing had happened.
Important applications of superposition principle :
(a) Interference of waves (b) Stationary waves (c) Beats.
 SureDen
SureDen