Refrigerator or Heat Pump
Refrigerator or Heat Pump
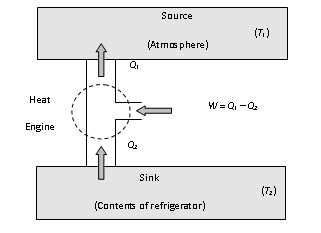
A refrigerator or heat pump is basically a heat engine run in reverse direction.
It essentially consists of three parts
Source : At higher temperature T1.
Working substance : It is called refrigerant liquid ammonia and freon works as a working substance.
Sink : At lower temperature T2.
The working substance takes heat Q2 from a sink (contents of refrigerator) at lower temperature, has a net amount of work done W on it by an external agent (usually compressor of refrigerator) and gives out a larger amount of heat Q1 to a hot body at temperature T1 (usually atmosphere). Thus, it transfers heat from a cold to a hot body at the expense of mechanical energy supplied to it by an external agent. The cold body is thus cooled more and more.
The performance of a refrigerator is expressed by means of “coefficient of performance” b which is defined as the ratio of the heat extracted from the cold body to the work needed to transfer it to the hot body.
i.e.
Therefore
A perfect refrigerator is one which transfers heat from cold to hot body without doing work
i.e. W = 0 so that Q1 = Q2 and hence β=∞
(1) Carnot refrigerator
For Carnot refrigerator Therefore
or
So coefficient of performance
where T1 = temperature of surrounding, T2 = temperature of cold body
It is clear that b = 0 when T2 = 0
i.e. the coefficient of performance will be zero if the cold body is at the temperature equal to absolute zero.
(2) Relation between coefficient of performance and efficiency of refrigerator
We know or
….. (i)
But the efficiency or
......(ii)
From (i) and (ii) we get
 SureDen
SureDen