Isothermal Process
Isothermal Process
When a gas undergoes expansion or compression at constant temperature, the process is called isothermal process.
Isothermal Process.
- When a thermodynamic system undergoes a physical change in such a way that its temperature remains constant, then the change is known as isothermal changes.
In this process, P and V change but T = constant i.e. change in temperature ΔT = 0
Essential condition for isothermal process
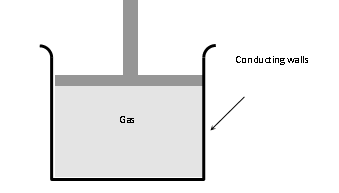
- (i) The walls of the container must be perfectly conducting to allow free exchange of heat between the gas and its surrounding.
- (ii) The process of compression or expansion should be so slow so as to provide time for the exchange of heat.
- Since these two conditions are not fully realised in practice, therefore, no process is perfectly isothermal.
- (2) Equation of state : From ideal gas equation PV = mRT
- If temperature remains constant then PV= constant i.e. in all isothermal process Boyle’s law is obeyed.
- Hence equation of state is PV = constant.
- (3) Example of isothermal process
- (i) Melting process [Ice melts at constant temperature 0°C]
- (ii) Boiling process [water boils at constant temperature 100°C].
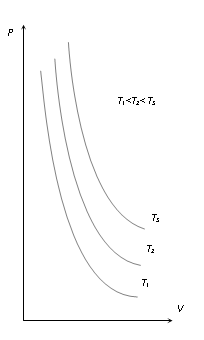
- (4) Indicator diagram
- (i) Curves obtained on PV graph are called isotherms and they are hyperbolic in nature.
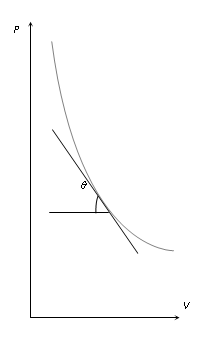
- (ii) Slope of isothermal curve : By differentiating PV = constant. We get
- PdV + VdP = 0 ⇒ PdV = -VdP ⇒dP/dV = -P/V
- Therefore tanθ = dP/dV = -P/V
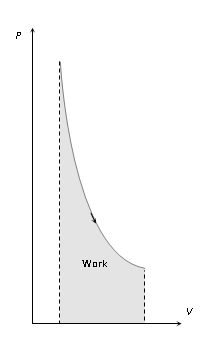
- (iii) Area between the isotherm and volume axis represents the work done in isothermal process.
- If volume increases ΔW = + Area under curve and if volume decreases ΔW = – Area under curve
- (5) Specific heat : Specific heat of gas during isothermal change is infinite.
- As C = Q/mΔT = Q/m x 0 = ∞ [As ΔT = 0]
- (6) Isothermal elasticity : For isothermal process PV = constant
- Differentiating both sides PdV + VdP = 0 ⇒ PdV = -VdP ⇒ P =dP/dV/V = Stress/ Strain = Eθ
- \ Eθ = P i.e. isothermal elasticity is equal to pressure
- At N.T.P. isothermal elasticity of gas = Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 x 105 N/m2
(7) Work done in isothermal process
-
[As PV = mRT]
-
-
- (8) FLTD in isothermal process
- ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW but ΔU ∝ ΔT
- Therefore ΔU = 0 [As ΔT = 0]
- Therefore ΔQ = ΔW i.e. heat supplied in an isothermal change is used to do work against external surrounding.
or if the work is done on the system than equal amount of heat energy will be liberated by the system.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen