Isobaric Process
Isobaric Process.
When a thermodynamic system undergoes a physical change in such a way that its pressure remains constant, then the change is known as isobaric process.
In this process V and T changes but P remains constant. Hence Charle’s law is obeyed in this process.
(1) Equation of state : From ideal gas equation PV = mRT
If pressure remains constant V µ T or V1/T1 = V2/T2 = constant
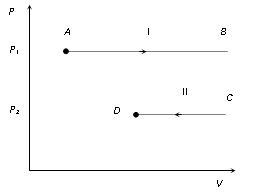
(2) Indicator diagram : Graph I represent isobaric expansion, graph II represent isobaric compression.
Slope of indicator diagram dP/dV = 0
(3) Specific heat : Specific heat of gas during isobaric process
(4) Bulk modulus of elasticity : [As ΔP = 0]
(5) Work done in isobaric process :
[As P = constant]
Therefore ΔW=P(Vf-Vi)= µR[Tf-Ti]= µRΔT
(6) FLTD in isobaric process :
and ΔW=µRΔT
From FLTD ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
Therefore
ΔQ = µCpΔT
 SureDen
SureDen