Time Period and Velocity
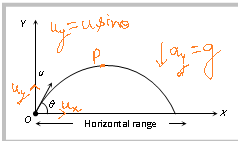
Oblique Projectile.
In projectile motion, horizontal component of velocity (u cos?), acceleration (g) and mechanical energy remains constant while, speed, velocity, vertical component of velocity (u sin ?), momentum, kinetic energy and potential energy all varies with time. Velocity, and Kinetic Energy are maximum at the point of projection while minimum (but not zero) at highest point.
Time of flight : The total time taken by the projectile to move from starting point to final point is called time of flight.
For vertical upward motion(Along Y axis)
0 = u sin? – gt
t = (u sin ? /g)
Now as time taken to go up(time of accent) is equal to the time taken to come down(time of descent) so
Time of flight T=2 t = (2u sin ?/g)
Time of flight can also be expressed as : T= 2 uy/g (where uy is the vertical component of initial velocity).
In general, T = 2v?/a?
Where v? and a? are the respective velocity and acceleration perpendicular to the surface.
Note: that if a projectile is thrown up an an inclined plane as shown in the fig.
Here v? = vo sinθ
And a? = g cos α
Thus, T = (2v?/a?)=(2vo sinθ/g cos α)
Instantaneous velocity v : Let vi be the instantaneous velocity of projectile at time t direction of this velocity is along the tangent to the trajectory at point P.
 SureDen
SureDen