Projectile Motion Intro
The motion of an object is called two dimensional, if two of the three co-ordinates are required to specify the position of the object in space changes w.r.t time and surroundings.
In such a motion, the object moves in a plane. For example, an insect crawling over the floor of a room, earth revolving around the sun etc.
Two special cases of motion in two dimension are 1. Projectile motion 2. Circular motion
PROJECTILE MOTION
Introduction.
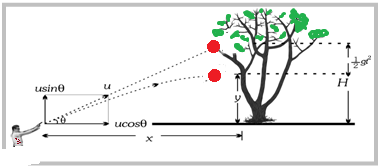
A hunter aims at fruit on a tree is an example of projectile motion.
The path of motion of a bullet will be parabolic and this motion of bullet is known as projectile motion.
If the force that acting on a particle acts at some angle with the direction of initial velocity, the resulting motion will be projectile motion
Projectile.
A body which is thrown at some angle with the horizontal and moves through the atmosphere but is not being propelled by any fuel is called projectile.
Example: (i) An arrow released from bow
(ii) A Javelin thrown by an athlete
Assumptions of Projectile Motion.
(1) Resistance due to air is negligible and will only be included if mentioned specially in the context.
(2) The effect due to curvature of earth is negligible.
(3) The effect due to rotation of earth is negligible.
(4) For all points of the trajectory, the acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ is constant in magnitude and direction.
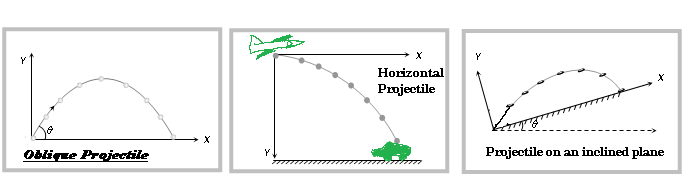
3.5 Types of Projectile Motion.
(1) Oblique projectile motion (2) Horizontal projectile motion (3) Projectile motion on an inclined plane
 SureDen
SureDen