Bulk Modulus
When a solid or fluid (liquid or gas) is subjected to a uniform pressure all over the surface, such that the shape remains the same, then there is a change in volume.
Then the ratio of normal stress to the volumetric strain within the elastic limits is called as Bulk modulus. This is denoted by K.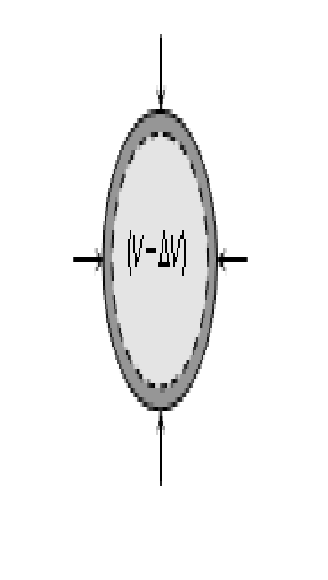
where p = increase in pressure; V = original volume; DV = change in volume
The negative sign shows that with increase in pressure p, the volume decreases by DV i.e. if p is positive, DV is negative. The reciprocal of bulk modulus is called compressibility.C = compressibility =
S.I. unit of compressibility is N–1m2 and C.G.S. unit is dyne–1cm2.
Gases have two bulk moduli, namely isothermal elasticity Eq and adiabatic elasticity Ef .
(1) Isothermal elasticity (Eq) : Elasticity possess by a gas in isothermal condition is defined as isothermal elasticity.
For isothermal process, PV = constant (Boyle’s law)
Differentiating both sides PdV + VdP = 0 Þ PdV = – VdP
Eq = P
i.e., Isothermal elasticity is equal to pressure.
(2) Adiabatic elasticity (Ef) : Elasticity possess by a gas in adiabatic condition is defined as adiabatic elasticity.
For adiabatic process, = constant
(Poisson’s law)
Differentiating both sides, Þ
Ef = g P
i.e., adiabatic elasticity is equal to g times pressure.
 SureDen
SureDen