Pascals Law
It states that if gravity effect is neglected, the pressure at every point of liquid in equilibrium of rest is same.
or
The increase in pressure at one point of the enclosed liquid in equilibrium of rest is transmitted equally to all other points of the liquid and also to the walls of the container, provided the effect of gravity is neglected.
Example : Hydraulic lift, hydraulic press and hydraulic brakes
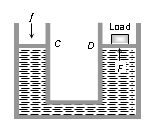
Working of hydraulic lift : It is used to lift the heavy loads. If a small force f is applied on piston of C then the pressure exerted on the liquid
[a = Area of cross section of the piston in C]
This pressure is transmitted equally to piston of cylinder D.
Hence the upward force acting on piston of cylinder D.
So heavy load placed on the larger piston is easily lifted upwards by applying a small force.
11.4 Archimedes Principle.
Accidentally Archimedes discovered that when a body is immersed partly or wholly in a fluid, in rest it is buoyed up with a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. This principle is called Archimedes principle and is a necessary consequence of the laws of fluid statics.
When a body is partly or wholly dipped in a fluid, the fluid exerts force on the body due to hydrostatic pressure. At any small portion of the surface of the body, the force exerted by the fluid is perpendicular to the surface and is equal to the pressure at that point multiplied by the area. The resultant of all these constant forces is called upthrust or buoyancy.
To determine the magnitude and direction of this force consider a body immersed in a fluid of density as shown in fig. The forces on the vertical sides of the body will cancel each other. The top surface of the body will experience a downward force.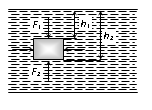
If L is the vertical height of the body
i.e., F = Weight of fluid displaced by the body.
This force is called upthrust or buoyancy and acts vertically upwards (opposite to the weight of the body) through the centre of gravity of displaced fluid (called centre of buoyancy). Though we have derived this result for a body fully submerged in a fluid, it can be shown to hold good for partly submerged bodies or a body in more than one fluid also.
(1) Upthrust is independent of all factors of the body such as its mass, size, density etc. except the volume of the body inside the fluid.
(2) Upthrust depends upon the nature of displaced fluid. This is why upthrust on a fully submerged body is more in sea water than in fresh water because its density is more than fresh water.
(3) Apparent weight of the body of density (P) when immersed in a liquid of density .Apparent weight = Actual weight – Upthrust
(4) If a body of volume V is immersed in a liquid of density then its weight reduces.
= Weight of the body in air, = Weight of the body in waterThen apparent (loss of weight)
 SureDen
SureDen