Force
Force
A pull or push which changes or tends to change the state of rest or of uniform motion or directionof motion of any object is called force. Force is the interaction between the object and the source.It is a vector quantity.
Effect of resultant force :
(1) may change only speed
(2) may change only direction of motion.
(3) may change both the speed and direction of motion.
(4) may change both the speed and direction of motion.
Unit of force : newton and kg m s-2 (MKS System)
dyne and g cm s-2 (CGS System)
1 newton = 105 dyne
Dimensional Formula of force : [M L T–2 ]
Types of Forces
Fundamental Forces: All the forces observed in nature such as muscular force, tension, friction, elastic, weight, electric, magnetic, nuclear, etc., can be explained in terms of only following four basic interactions:
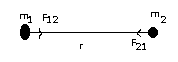
a)Gravitational Force: The force of interaction which exists between two particles of masses m1 and m2, due to their masses is called gravitational force.
F=Gm1m2/r2
G= universal gravitational constant = 6.67 × 10–11 Nm2/kg2.
b) Eletromagnetic Force: Force exerted by one particle on the other because of the electric charge onthe particles or due to magnetic properties of material is called electromagnetic force.
c) Nuclear Force : It is the strongest force. It keeps nucleons (neutrons and protons) together inside the nucleus inspite of large electric repulsion between protons.It acts within the nucleus that too upto a very small distance.
d) Weak Force: It acts between any two elementary particles. Under its action a neutron can change into a proton emitting an electron and a particle called antineutrino. The range of weak force is very small, in fact much smaller than the size of a proton or a neutron.
FN:FEM:FW:FG ∷ 1:10-2:10-7:10-38
Classification of forces on the basis of contact :
(A) Field Force:
Force which acts on an object at a distance by the interaction of the object with the field produced by other object is called field force. Examples
(a) Gravitation force
(b) Electromagnetic force
Contact Force: Forces which are transmitted between bodies by short range atomic molecular interactions are called contact forces. When two objects come in contact they exert contact forces on each other.
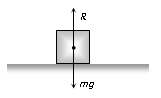
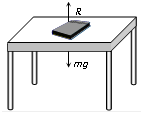
(i) Normal force (N): It is the component of contact force perpendicular to the surface. It measures how strongly the surfaces in contact are pressed against each other. It is the electromagnetic force.
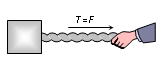
(ii) Tension(T):Tension in a string is a electromagnetic force. It arises when a string is pulled. If a massless string is not pulled, tension in it is zero.
(iii) Frictional Force: It is the component of contact force tangential to the surface. It opposes the relative motion of the two surfaces in contact.
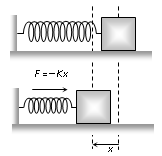
(iv) Spring force : Every spring resists any attempt to change its length. This resistive force increases with change in length. Spring force is given by; where x is the change in length and K is the spring constant (unit N/m).
 SureDen
SureDen