Newton Law of Gravitation
Newton's law of Gravitation.
Newton's law of gravitation states that every body in this universe attracts every other body with a force, which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres.
The direction of the force is along the line joining the particles. That is why Gravitational force is a Central Notes.
F ∝ (m1m2/r2)
or F = G(m1m2/r2)
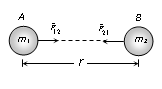
Vector form :
Similarly
= unit vector from A to B
= unit vector from B to A,
= gravitational force exerted on body A by body B
= gravitational force exerted on body B by body A
It is clear that
= –
Which is Newton's third law of motion.
Here G is constant of proportionality which is called 'Universal gravitational constant'.
Note:
(a) The value of G is 6.67×10–11N–m2kg–2 in S.I. and 6.67×10–8dyne- cm2-g–22 – t–––– in C.G.S. system.
(b) Dimensional formula [M-1L3T-2].
(c) The value of G does not depend upon the nature and size of the bodies.
(d) It also does not depend upon the nature of the medium between the two bodies.
Properties of Gravitational Force.
(1) It is always attractive in nature .
(2) It is independent of the medium between the particles
(3) It is a long range force.
(4) It is a central force .
(5) It is a two-body interaction i.e. gravitational force between two particles is independent of the presence or absence of other particles; so the principle of superposition is valid i.e. force on a particle due to number of particles is the resultant of forces due to individual particles i.e.
(6) It is the weakest force in nature.
(8) It is a conservative force .
 SureDen
SureDen