Keplers Laws
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion.
Planets are large natural bodies rotating around a star(sun in case of milky way) in definite orbits. Our planetary system is called solar system which consists of eight planets, viz., Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Out of these planets Mercury is the smallest and closest to the sun. Jupiter is largest and has maximum number of moons (12). Venus is closest to Earth and brightest.
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion
(1) The law of Orbits : Every planet moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit with sun at one of the foci.
(2) The law of Areas : The line joining the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal interval of time. i.e. areal 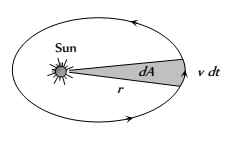 velocity is constant. According to this law planet will move slowly when it is farthest from sun and more rapidly when it is nearest to sun. It is based on law of conservation of angular momentum.
velocity is constant. According to this law planet will move slowly when it is farthest from sun and more rapidly when it is nearest to sun. It is based on law of conservation of angular momentum.
Areal velocity =
(Area of a sector = (1/2)radius x Arc Length
[As L=mvr , rv = L/m]
(3) The law of periods : The square of period of revolution (T) of any planet around sun is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the orbit.
T2 α a3 or
2a = r1 + r2
where a = semi-major axis
r1 = Shortest distance of planet from sun (Perigee).
r2 = Largest distance of planet from sun (Apogee).
Note:: Kepler's laws are also valid for satellites.
 SureDen
SureDen