Mode of Transference of energy
Mode of Transference of energy
If energy generally transfers occur in 2 modes →
In terms of heat
In terms of work
(1) Heat is always transferred from higher temp. to lower temp. If a system is at higher temperature Then lost heat to the surroundings while if surrounding is at higher temp., then heat is transfers to the system which is at lower temp.
(2) Work is defined as product of force & displacement of the object in the direction of force
dW = F.ds
& unit of work in SI system is Joule.
Although work is of diff. types
If m is the mass of body & h is the height of the object & g force gravity
(1) Gravitational work w = mgh → When a body moves through a certain distance, gravitational work is said to be done.
(2) Electrical work → E x Q. (Charge)
(Potential different)
Similarly, electrical work is said to be done when a electrical current is flowing through the circuit.
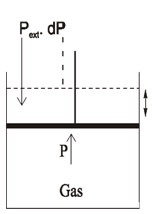
(3) Mechanical work → The work of expansion or contraction is known as Mechanical Work
Work of expansion
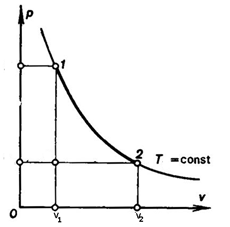
Isothermal, Reversible Expansion of the gas
W = -P & V
PV = nRt
P = nRT/P ― (2)
W = - nRT [loge V2 – loge V1]
W = - 2.303 nRT [loge V2 – loge V1]
W = - 2.303 nRT [log10 (V2/V1)]
Numerical: Calculate the amount of work done when two moles of an ideal gas expand Isothermally & reversibly at 298 K. from a V = 1 to V = 20 L log2 = 0.3010
W = -2.303 x 2 x 8.314 x 298 x log (20/10)
= -2.303 x 2 x 8.314 x 298 x 0.301.
= 3434.920
Enthalpy
It is defined as the sum of the internal energy should within a substance + pressure – volume work. It is denoted by H.
H = E + PV → enthalpy
 SureDen
SureDen