Filling of Orbitals
Filling of Orbitals in atoms-
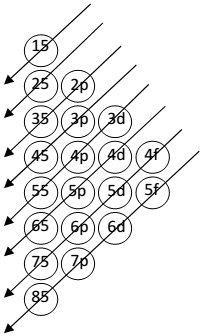
- Aufbau principle – aufbau = German word means building up.
“The orbitals are filled in order of their increasing energies.”
The order of increasing energies of various orbitals calculated by (n+l) rule .
- Lower the value of (n+l) for an orbital, lower the energy.
- If two different orbital having same value of (n+l), the orbital
with lower value of n, has lower energy.
e.g.
|
4s |
3d |
2p |
3s |
|
n=4 |
n=3 |
n=2 |
n=3 |
|
l=0 |
l=2 |
l=1 |
l=0 |
|
n+l=4 |
n+l=5 |
n+l=3 |
n+l=3 |
2) Pauli exclusion principle-
Pauli exclusion principle- given by Wolfgang Pauli
“No two electrons in an atom can have all the set of four quantum numbers same”
i.e. for any 2 electron , 3 quantum numbers are same but 4th must be different.
e.g. n=3, l=0, m=0, s=+1/2
n=3, l=0, m=0, s=-1/2
i.e. An orbital can have a maximum 2 electrons and these must have opposite spins is called Pauli exclusion principle.
Pauli exclusion principle is called exclusion principle because if one electron in an atom has particular value for the 4 quantum number then all the other electros in that atom are excluded from having the same set of values.
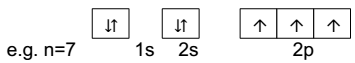
3) Hunds rule of maximum multiplicity- (for degenerate orbitals)
Electron pairing in p, d and f orbitals
Can’t occur until each orbital of a given subshell contains are electron each.
Electron pairing starts with 4th, 6th, 8th electron in p, d and f orbital respectively.
Maximum multiplicity means total spin of unpaired electron is maximum.
Electron being identical in charges, repel each other when present in same orbital and total spin
This repulsion can be minimized if two electrons move as for as possible, further if 2 electron in different orbital show less inter electronic repulsion.
 SureDen
SureDen