Discovery of Atom
According to John Dalton, matter was made up of extremely small invisible particles called atoms (Greek word) atom means unstable. But according to J.J.Thomson , Goldstein, Rutherford, Chadwick, Bohr other eminent scientist prove that atom was no the smallest indivisible particle but had a complex structure and is made up of electrons, protons & neutrons. At present about 35 different subatomic particles are known but electron, proton & neutron are regarded as fundamental particles.
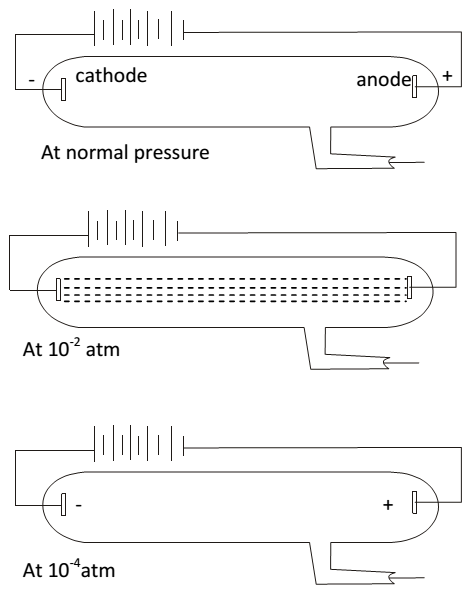
Discovery of electron-(cathode rays ) in 1859 Julius Plucker observed that at ordinary conditions gases are poor conductor of electricity. However when high voltage of low pressure is applied in a discharge tube gas becomes conductor of electricity is produced in the form of rays. These rays are produced by the cathode + move towards the anode called cathode rays. These rays are shown by scientists Luke Plucker, Crooks. But main credit goes to J.J. Thomson. He studied the proof of cathode rays in detail which leads to the discovery of electron.
For this purpose, a cylindrical hard class tube (about 50cm) long closed at both ends is taken. This tube is called discharge tube or crook’s tube. It is fitted with metallic electrodes. Discharge tube has a side tube through which it can be evaluated to any desired pressure, with the keep of vacuum pump. When a high voltage of about 10000 V is applied between the electrode , the following results are observed at different pressure.
Proof of cathode rays – J.J. Thomson studied properties of cathode rays. Some important properties are.
- Cathode rays travel in straight line
- Cathode rays producing heating effect
- Cathode rays consists of material particles + gave mechanical power
- Cathode rays are negatively charged
- They cause ionization of the gas through which they pass.
- They produce –x- rays when they strike against Tungsten or Molybdenum
- They produce green fluorescence on the glass walls of the discharge tube as well as on phosphorescent of Fluorescent substances like ZnS.
- They affect the photographic plates
- They possess penetration effect (pass into thin foil )
Thus negatively charged material consisting the cathode rays are called electrons.
Use of cathode rays – Television picture tube is a cathode ray tube in which picture is produce to Fluorescence
Fluorescent light tube are also called cathode ray tubes.
Determination of ratio of charge/mass of electrons J.J.Thomson determine the ratio of charge to mass of electron under the influence of electric + mag. field with high potential difference between cathode + anode
e/m of electron= 1.76 x 108 c/g
the charge on the electron was found by R.A.Millkan with the help of oil drop experiment
charge on an electron = 1.602 x 10-19 e
from the value of e and e/m, the mass of the electron was determined by dividing e by e/m. Thus
this is called rest mass of electron because it has been calculated assuming that the electrons is moving with a velocity much less than the velocity of light.
The mass of electron is much smaller than the mass of hydrogen. It has been found that the mass of electron is approximately 1/1837 mass of an atom of hydrogen. Such fundamental particle which carries one unit – negative charge mass equal to 1/1837 of that Hydrogen atom called Electron.
 SureDen
SureDen