Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom
Bohr model of atom – (Based upon Planck’s Quantum theory)
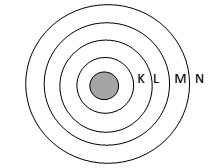
Main postulates – (1) Electron in a atom revolve around the nucleus only in a certain selected circular path called orbits. These orbits having definite energy. Hence called as Energy Shells. They are designated as K L M N shells.
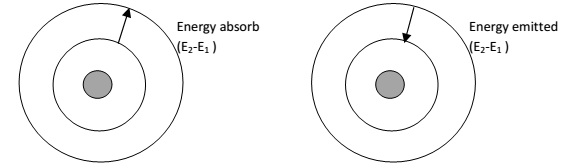
- The revolving electron can emit or absorb energy only in fixed amount or packets called Quanta.
- Under suitable conditions, when energy is supplied to an atom, electron jump from lower to lighter energy state. The lighter state of electron is called existed state.
- Electron in existed state has a tendency to jump back to the lower energy state it radiates the same amount of energy absorbed.
- The energy emitted or absorbed in quanta is equal to the difference between energies of two energy levels.
ΔE = E2-E1
E1 & E2
- Only those orbits are permitted in which the regular momentum of electron is a whole no. multiple of h/2π .
If n = 1 then = h/2π
If n = 2 then = h/π
if n = 3 then = 3h/2π
if n = 4 then = 2h/π
This postulate constitute energy is the key concept of Bohr’s theory. Quantization mean that a quantity can’t change gradually and continuously to have any arbitrary valve but changes only abruptly and discontinuously to have certain definite or discrete value.
Related Keywords
 SureDen
SureDen