Inter molecular forces
Inter molecular forces →
There are the forces of attraction between molecules of same or different substances. There are of following types →
(1) Dipole – Dipole interactions exist among polar molecules. Whose positive end of one molecule attracts negative and of other molecule e.g. among HCl molecule
→ Increases the polarity of molecules increases is dipole-dipole inter atoms.
→ These are also brown as keesom forces and effect is known as orientation effect.
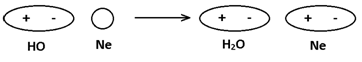
(ii) Dipole – induced dipole interaction → Such forces are present between polar and non polar molecules and polar molecules induce polarity is non-polar molecules and are attracted. e.g. bet. so and Ne,
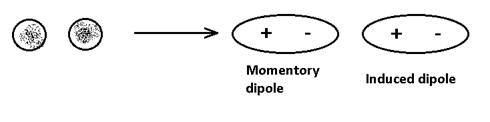
(iii) Induced – dipole – induce dipole or London or Dispersion forces which exist between non-polar molecules. Where at any instant of time, the electron cloud is distorted to produce momentary dipole in one molecule which induced dipole is neighbouring molecules and hence attracted. e.g. liquid N2, liquid He etc.
Energy of interaction varies as (1/r6). Where r → distance between particles
(iv) Ion – Dipole interactions → Are present between ions and polar molecules e.g. I- H2O, NO3 and H2O
(v) Ion – induced dipole interactions are found between ions and non-polar molecular e.g. No3-2 and I2
→ London forces are the weakest forces. The size of molecules increases London forces also increase.
→ The thermal energy possessed by the molecules due to temperature results into movement of molecules.
→ In gases, intermolecular forces are weakest & thermal energy is maximum.
→ In solids inter mol. forces are stronger and thermal energy is minimum.
→ In liquids two types of energies are inter mediate between those of gases and solids.
Solids → liquid → gas
→Increases thermal energy
 SureDen
SureDen