Redox reactions and electrode processes
Redox reactions and electrode processes:
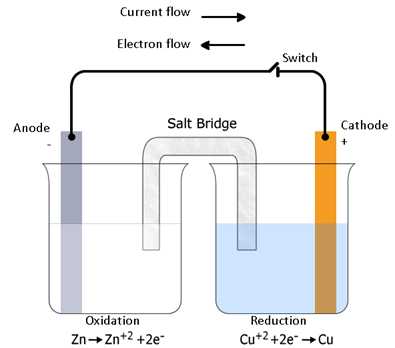
If zinc rod is dipped in copper sulphate solution. The redox reaction takes place and during the reaction, zinc is oxidized to zinc ions and copper ions are reduced to metallic copper due to direct transfer of electrons from zinc to copper ion. During this reaction heat is also evolved.
We take copper sulphate solution in a beaker and put a copper strip or rod in it. We also zinc sulphate solution in another beaker and put a zinc rod or strip in it.
Now reaction takes place in either of the beakers
Having together the oxidized and reduced forms of a substance taking part in an oxidation or reduction half reaction.
Now, 2 reactions are occurring here.
In first beaker →
Oxidation:- Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
In other beaker →
Reduction:- Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
We connect these 2 beakers by a (v – tube containing a solution of potassium chloride or ammonium nitrate with agar – agar) called salt bridge.
This salt bridge connects both solutions for electron transfer between them & also disallow both solutions to mix.
Zinc & copper rods are connected by metallic wire with ammeter & switch.
This set up is called Daniell cell.
(1) Here, electron transfer takes place from Zn to Cu2+ through metallic wire connecting the 2 rods.
(2) Here current flow occurs by migration of ions through salt bridge only, if there is potential difference.
(3) An direction of flow of current is opposite of electron flow.
(4) In anode (Zn sulphate solution) electrons are produced that travels to cathode (Cu sulphate solution) and reduces the Cu2+ to Cu. These electrons travels through ext. circuit of wires.
 SureDen
SureDen